CXC chemokine receptor 4 is expressed in uveal malignant melanoma and correlates with the epithelioid-mixed cell type
- PMID: 17410362
- PMCID: PMC11030263
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-007-0303-6
CXC chemokine receptor 4 is expressed in uveal malignant melanoma and correlates with the epithelioid-mixed cell type
Abstract
Purpose: Although relatively rare, uveal melanoma is the most common ocular tumor of adults. Up to half of uveal melanoma patients die of metastatic disease. CXCR4, a chemokine receptor, is a prognostic factor in cutaneous melanoma involved in angiogenesis and metastasis formation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of CXCR4 in uveal melanoma.
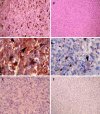
Methods: CXCR4 was detected by immunohistochemistry in 44 samples of uveal melanoma. Staining was categorized into three semiquantitative classes based on the rate of stained (positive) tumor cells: absence of staining, <50% of cell (+) and >50% (++). Correlations between CXCR4 expression, data on patient and tumor features were studied by contingency tables and the chi2 test. Time-to-event curves were studied using the Kaplan-Meier method. Univariate analysis was performed using the log-rank test. Ninety-five percent confidence intervals (95% CI) of hazard ratios were also reported.
Results: Staining for CXCR4 protein was absent in 18 tumors (40.9%), present in <50% of cells in 19 (43.2%) and in >50% of cells in 7 (15.9%) tumors. CXCR4 expression correlated to the epithelioid-mixed cell type (P=0.030). No statistically significant relation emerged between CXCR4 expression, largest tumor diameter (LTD) and extracellular matrix patterns as evaluated through histological patterns stained with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS). Events occurred in 2 out of 18 patients (11.1%) with negative tumors (2 deaths), in 3 out of 19 patients (15.8%) with <50% of positive tumor cells (2 deaths and 1 occurrence of metastases) and in 1 out of 7 patients (14.3%) with >50% of positive tumor cells (1 occurrence of metastases). The cell type (P=0.0457) but not CXCR4 showed prognostic value at univariate analysis.
Conclusion: This study shows that CXCR4 is commonly expressed in uveal melanoma and correlates with cell type a well-established prognostic factor.
Figures

References
-
- Harbour JW. Clinical overview of uveal melanoma: introduction to tumors of the eye. In: Albert DM, Polans A, editors. Ocular oncology. Marcel Dekker: New York; 2003. pp. 1–18.
-
- Callender GR Malignant melanotic tumors of the eye: a study of histologic types in 111 cases. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1931;36:131–142.
-
- Zimmerman LE, McLean IW. An evaluation of enucleation in the management of uveal melanomas. Am J Ophthalmol. 1979;87:741–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

