Pericentric chromatin is an elastic component of the mitotic spindle
- PMID: 17412588
- PMCID: PMC1937037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.03.033
Pericentric chromatin is an elastic component of the mitotic spindle
Abstract
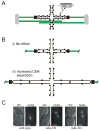
Background: Prior to chromosome segregation, the mitotic spindle bi-orients and aligns sister chromatids along the metaphase plate. During metaphase, spindle length remains constant, which suggests that spindle forces (inward and outward) are balanced. The contribution of microtubule motors, regulators of microtubule dynamics, and cohesin to spindle stability has been previously studied. In this study, we examine the contribution of chromatin structure on kinetochore positioning and spindle-length control. After nucleosome depletion, by either histone H3 or H4 repression, spindle organization was examined by live-cell fluorescence microscopy.
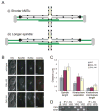
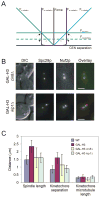
Results: Histone repression led to a 2-fold increase in sister-centromere separation and an equal increase in metaphase spindle length. Histone H3 repression does not impair kinetochores, whereas H4 repression disrupts proper kinetochore function. Deletion of outward force generators, kinesins Cin8p and Kip1p, shortens the long spindles observed in histone-repressed cells. Oscillatory movements of individual sister chromatid pairs are not altered after histone repression.
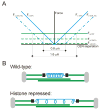
Conclusions: The increase in spindle length upon histone repression and restoration of wild-type spindle length by the loss of plus-end-directed motors suggests that during metaphase, centromere separation and spindle length are governed in part by the stretching of pericentric chromatin. Chromatin is an elastic molecule that is stretched in direct opposition to the outward force generators Cin8p and Kip1p. Thus, we assign a new role to chromatin packaging as an integral biophysical component of the mitotic apparatus.
Figures

Comment in
-
Mitosis: springtime for chromatin.Curr Biol. 2007 Jun 19;17(12):R460-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.04.019. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17580075
References
-
- Scholey JM, Brust-Mascher I, Mogilner A. Cell division. Nature. 2003;422:746–752. - PubMed
-
- Lew DJ, Burke DJ. The spindle assembly and spindle position checkpoints. Annu Rev Genet. 2003;37:251–282. - PubMed
-
- Goshima G, Yanagida M. Establishing biorientation occurs with precocious separation of the sister kinetochores, but not the arms, in the early spindle of budding yeast. Cell. 2000;100:619–633. - PubMed
-
- Pearson CG, Yeh E, Gardner M, Odde D, Salmon ED, Bloom K. Stable kinetochore-microtubule attachment constrains centromere positioning in metaphase. Curr Biol. 2004;14:1962–1967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

