Type 1 diabetes and pregnancy
- PMID: 17413175
- PMCID: PMC1847857
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39154.700417.BE
Type 1 diabetes and pregnancy
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
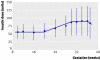
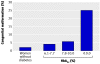
Similar articles
-
Pregnancy management in women with insulin-dependent diabetes.Br J Hosp Med. 1997 Sep 3-16;58(5):207-10. Br J Hosp Med. 1997. PMID: 9488816 Review. No abstract available.
-
Management of diabetes from preconception to the postnatal period: summary of NICE guidance.BMJ. 2008 Mar 29;336(7646):714-7. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39505.641273.AD. BMJ. 2008. PMID: 18369227 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Caring for pregnant women whose diabetes antedates pregnancy: is there room for improvement?Diabetologia. 2018 May;61(5):1022-1026. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4565-7. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29411042 No abstract available.
-
Advances in management of Type 1 diabetes and pregnancy.Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Dec;11(6):557-62. doi: 10.1097/00001703-199912000-00004. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10674832 Review.
-
Type 1 diabetes & pregnancy.Adv NPs PAs. 2011 Nov;2(11):20-3. Adv NPs PAs. 2011. PMID: 22128676 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes among non-pregnant women of reproductive age in the United States, 1999-2010.Prim Care Diabetes. 2015 Feb;9(1):71-3. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Prim Care Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 24216319 Free PMC article.
-
Homing receptor expression is deviated on CD56+ blood lymphocytes during pregnancy in Type 1 diabetic women.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0119526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119526. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25793768 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal and infant mortality in term and preterm births among women with type 1 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2011 Nov;54(11):2771-8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2281-7. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21866407
-
Preventable health and cost burden of adverse birth outcomes associated with pregestational diabetes in the United States.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Jan;212(1):74.e1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.09.009. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015. PMID: 25439811 Free PMC article.
-
Renal efflux transporter expression in pregnant mice with Type I diabetes.Toxicol Lett. 2012 Jun 20;211(3):304-11. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Toxicol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22531820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carron-Brown S, Kyne-Grzebalski D, Mwangi B, Taylor R. Effect of management policy upon 120 type 1 diabetic pregnancies: policy decisions in practice. Diabet Med 1999;16:573-8. - PubMed
-
- Penney GC, Mair G, Pearson DW. Outcomes of pregnancies in women with type 1 diabetes in Scotland: a national population-based study. BJOG 2003;110:315-8. - PubMed
-
- Jensen DM, Damm P, Moelsted-Pedersen L, Ovesen P, Westergaard JG, Moeller M, et al. Outcomes in type 1 diabetic pregnancies: a nationwide, population-based study. Diabetes Care 2004;27:2819-23. - PubMed
-
- Temple RC, Aldridge VJ, Murphy HR. Prepregnancy care and pregnancy outcomes in women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1744-9. - PubMed
-
- Taylor R, Lee C, Kyne-Grzebalski D, Marshall SM, Davison JM. Clinical outcomes of pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:537-41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
