Automated discrimination between very early Alzheimer disease and controls using an easy Z-score imaging system for multicenter brain perfusion single-photon emission tomography
- PMID: 17416830
- PMCID: PMC7977345
Automated discrimination between very early Alzheimer disease and controls using an easy Z-score imaging system for multicenter brain perfusion single-photon emission tomography
Abstract
Background and purpose: In Alzheimer disease (AD), a peculiar regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) abnormality has been reported in the posterior cingulate gyri and precunei, even at a very early stage. We performed a multicenter brain perfusion single-photon emission tomography (SPECT) study to evaluate the discrimination ability of an easy Z-score imaging system (eZIS) with a common normal data base between patients with very early AD at the stage of mild cognitive impairment and age-matched healthy controls.
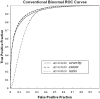
Materials and methods: For a multicenter study, SPECT images of 40 patients with AD and 40 healthy volunteers were acquired from 4 gamma camera systems in 4 different institutions. Systematic differences of SPECT images between gamma cameras were corrected by using conversion maps calculated from the SPECT images of the same brain phantom. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to discriminate patients and controls by using a Z-score in the volume of interest (VOI), which had been defined as a region related to AD in subjects other than those in a multicenter study.
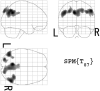
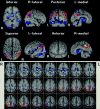
Results: Bilateral posterior cingulate gyri, precunei, and parietal cortices were defined as a VOI showing rCBF reduction in very early AD. A new indicator of rCBF abnormality in the VOI provided 86% accuracy for distinction of AD and healthy controls in the multicenter study. The area under the ROC curve was 0.934.
Conclusion: Because an eZIS can use a common normal data base by converting site-specific SPECT data to the core data, the eZIS was useful for automated diagnosis of very early AD in routine studies in multiple institutions.
Figures
References
-
- Minoshima S, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. Posterior cingulate cortex in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 1994;344:895 - PubMed
-
- Minoshima S, Giordani B, Berent S, et al. Metabolic reduction in the posterior cingulate cortex in very early Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 1997;42:85–94 - PubMed
-
- Johnson KA, Jones K, Holman BL, et al. Preclinical prediction of Alzheimer's disease using SPECT. Neurology 1998;50:1563–71 - PubMed
-
- Kogure D, Matsuda H, Ohnishi T, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of early Alzheimer's disease using brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 2000;41:1155–62 - PubMed
-
- Imabayashi E, Matsuda H, Asada T, et al. Superiority of 3-dimensional stereotactic surface projection analysis over visual inspection in discrimination of patients with very early Alzheimer's disease from controls using brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1450–57 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
