The medial temporal lobe and recognition memory
- PMID: 17417939
- PMCID: PMC2064941
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.30.051606.094328
The medial temporal lobe and recognition memory
Abstract
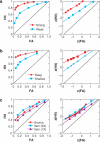
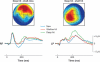
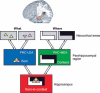
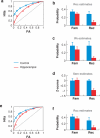
The ability to recognize a previously experienced stimulus is supported by two processes: recollection of the stimulus in the context of other information associated with the experience, and a sense of familiarity with the features of the stimulus. Although familiarity and recollection are functionally distinct, there is considerable debate about how these kinds of memory are supported by regions in the medial temporal lobes (MTL). Here, we review evidence for the distinction between recollection and familiarity and then consider the evidence regarding the neural mechanisms of these processes. Evidence from neuropsychological, neuroimaging, and neurophysiological studies of humans, monkeys, and rats indicates that different subregions of the MTL make distinct contributions to recollection and familiarity. The data suggest that the hippocampus is critical for recollection but not familiarity. The parahippocampal cortex also contributes to recollection, possibly via the representation and retrieval of contextual (especially spatial) information, whereas perirhinal cortex contributes to and is necessary for familiarity-based recognition. The findings are consistent with an anatomically guided hypothesis about the functional organization of the MTL and suggest mechanisms by which the anatomical components of the MTL interact to support the phenomenology of recollection and familiarity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imaging recollection and familiarity in the medial temporal lobe: a three-component model.Trends Cogn Sci. 2007 Sep;11(9):379-86. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.08.001. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007. PMID: 17707683 Review.
-
The medial temporal lobe.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:279-306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.27.070203.144130. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15217334 Review.
-
Modulation of encoding and retrieval by recollection and familiarity: mapping the medial temporal lobe networks.Neuroimage. 2011 Oct 15;58(4):1131-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.086. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21763430
-
Triple dissociation in the medial temporal lobes: recollection, familiarity, and novelty.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Oct;96(4):1902-11. doi: 10.1152/jn.01029.2005. Epub 2006 May 31. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16738210
-
Visual perception and memory: a new view of medial temporal lobe function in primates and rodents.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:99-122. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.113046. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17417938 Review.
Cited by
-
Multisensory integration and belief in the self.Front Psychol. 2022 Oct 13;13:983592. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.983592. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36312078 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The role of relational binding in item memory: evidence from face recognition in a case of developmental amnesia.J Neurosci. 2015 Apr 1;35(13):5342-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3987-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25834058 Free PMC article.
-
The very same thing: Extending the object token concept to incorporate causal constraints on individual identity.Adv Cogn Psychol. 2012;8(3):234-47. doi: 10.2478/v10053-008-0119-8. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Adv Cogn Psychol. 2012. PMID: 22956989 Free PMC article.
-
Remembering with gains and losses: effects of monetary reward and punishment on successful encoding activation of source memories.Cereb Cortex. 2014 May;24(5):1319-31. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs415. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Cereb Cortex. 2014. PMID: 23314939 Free PMC article.
-
Single neuron activity and theta modulation in postrhinal cortex during visual object discrimination.Neuron. 2012 Dec 6;76(5):976-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.039. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23217745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addis DR, Moscovitch M, Crawley AP, McAndrews MP. Recollective qualities modulate hippocampal activation during autobiographical memory retrieval. Hippocampus. 2004;14:752–62. - PubMed
-
- Aggleton JP, Brown MW. Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behav. Brain Sci. 1999;22:425–44. - PubMed
-
- Aggleton JP, Vann SD, Denby C, Dix S, Mayes AR, et al. Sparing of the familiarity component of recognition memory in a patient with hippocampal pathology. Neuropsychologia. 2005;43(12):1810–23. - PubMed
-
- Bar M, Aminoff E. Cortical analysis of visual context. Neuron. 2003;38:347–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

