Antiphospholipid antibodies and pregnancy loss: a disorder of inflammation
- PMID: 17418423
- PMCID: PMC2247372
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jri.2007.02.007
Antiphospholipid antibodies and pregnancy loss: a disorder of inflammation
Abstract
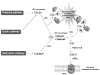
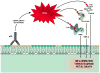
The antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a leading cause of miscarriage and maternal and fetal morbidity. APS is characterized by thrombosis and pregnancy loss that occur in the presence of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies. Using a mouse model of APS induced by passive transfer of human aPL antibodies, we have shown that complement activation plays an essential and causative role in pregnancy loss and fetal growth restriction, and that blocking activation of the complement cascade rescues pregnancies. Conventional treatment for APS patients is sub-anticoagulant doses of heparin throughout pregnancy. Could heparin prevent pregnancy loss by inhibiting complement? In our experimental model of APS, heparin inhibits activation of complement on trophoblasts in vivo and in vitro, and anticoagulation in and of itself is not sufficient to prevent pregnancy complications. These studies underscore the importance of inflammation in fetal injury associated with aPL antibodies and raise the importance of developing and testing targeted complement inhibitory therapy for patients with APS.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pober JS. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. W.B. Saunders Company; Philadelphia, PA: 2000. pp. 316–334.
-
- Berman J, Girardi G, Salmon JE. TNF-alpha is a critical effector and a target for therapy in antiphospholipid antibody-induced pregnancy loss. J Immunol. 2005;174:485–490. - PubMed
-
- Brown EJ. Complement receptors and phagocytosis. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991;3:76–82. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham DS, Tichenor JR., Jr Decay-accelerating factor protects human trophoblast from complement-mediated attack. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995;74:156–161. - PubMed
-
- Derksen RH, Khamashta MA, Branch DW. Management of the obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthr Rheum. 2004;50:1028–1039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

