Inhibition of cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis, reactivation of DLC1, and modulation of other gene expression by dietary flavone in breast cancer cell lines
- PMID: 17418982
- PMCID: PMC1950447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cdp.2007.02.005
Inhibition of cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis, reactivation of DLC1, and modulation of other gene expression by dietary flavone in breast cancer cell lines
Abstract
Background: Dietary flavone was previously shown to increase the expression of deleted in liver cancer-1 gene (DLC-1) in HT-29 colon carcinoma cell line [Herzog A, Kindermann B, Doring F, Daniel H, Wenzel U. Pleiotropic molecular effects of the pro-apoptotic dietary constituent flavone in human colon cancer cells identified by protein and mRNA expression profiling. Proteomics 2004;4:2455-64]. DLC-1 that encodes a Rho GTPase-activating protein, functions as a tumor suppressor gene and is frequently inactivated or down-regulated in several common cancers. Restoration of DLC-1 expression suppresses in vitro tumor cells proliferation and tumorigenicity in vivo.
Methods: Here, the effect of flavone was examined in several DLC-1-deficient cell lines derived from different types human cancer using assays for cell proliferation, gene expression and transfer.
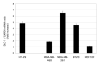
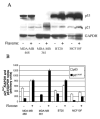
Results: We show that exposure to 150 microM flavone increased DLC1 expression in breast but not in liver or prostate carcinoma cells or a nonmalignant breast epithelial cell line. Flavone restored the expression of DLC1 in the breast carcinoma cell lines MDA-MB-468, MDA-MB-361, and BT20 as well as in the colon carcinoma cell line HT-29 all of which are DLC-1-negative due to promoter hypermethylation. We further show that flavone inhibited cell proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest at G(2)-M, increased p21(Waf1) gene expression, and caused apoptosis. Microarray analysis of these aggressive and metastatic breast carcinoma cells revealed 29 flavone-responsive genes, among which the DNA damage-inducible GADD genes were up-regulated and the proto-oncogene STMN1 and IGFBP3 were down-regulated.
Conclusions: Flavone-mediated alterations of genes that regulate tumor cell proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis contribute to chemopreventive and antitumoral effects of flavone. Alone or in combination with demethylating agents, flavone may be an effective adjunct to chemotherapy in preventing breast cancer metastasis.
Figures


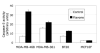


References
-
- Yuan BZ, Miller MJ, Keck CL, Zimonjic DB, Thorgeirsson SS, Popescu NC. Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a gene frequently deleted in human liver cancer (DLC-1) homologous to rat RhoGAP. Cancer Res. 1998;58:2196–99. - PubMed
-
- Seng TJ, Low JS, Li H, Cui Y, Goh HK, Wong ML, et al. The major 8p22 tumor suppressor DLC1 is frequently silenced by methylation in both endemic and sporadic nasopharyngeal, esophageal, and cervical carcinomas, and inhibits tumor cell colony formation. Oncogene advance online publication. 2006 July 24; doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209839. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Syed V, Mukherjee K, Lyons-Weiler J, Lau KM, Mashima T, Tsuruo T, et al. Identification of ATF-3, caveolin-1, DLC-1, and NM23-H2 as putative antitumorigenic, progesterone-regulated genes for ovarian cancer cells by gene profiling. Oncogene. 2005;24:1774–87. - PubMed
-
- Wong CM, Yam JW, Ching YP, Yau TO, Leung TH, Jin DY, et al. Rho GTPase-activating protein deleted in liver cancer suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8861–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

