Stereologic estimates of total spinophilin-immunoreactive spine number in area 9 and the CA1 field: relationship with the progression of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 17420070
- PMCID: PMC2569870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.03.007
Stereologic estimates of total spinophilin-immunoreactive spine number in area 9 and the CA1 field: relationship with the progression of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
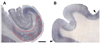
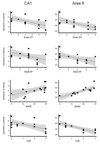
The loss of presynaptic markers is thought to represent a strong pathologic correlate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Spinophilin is a postsynaptic marker mainly located to the heads of dendritic spines. We assessed total numbers of spinophilin-immunoreactive puncta in the CA1 and CA3 fields of hippocampus and area 9 in 18 elderly individuals with various degrees of cognitive decline. The decrease in spinophilin-immunoreactivity was significantly related to both Braak neurofibrillary tangle (NFT) staging and clinical severity but not A beta deposition staging. The total number of spinophilin-immunoreactive puncta in CA1 field and area 9 were significantly related to MMSE scores and predicted 23.5 and 61.9% of its variability. The relationship between total number of spinophilin-immunoreactive puncta in CA1 field and MMSE scores did not persist when adjusting for Braak NFT staging. In contrast, the total number of spinophilin-immunoreactive puncta in area 9 was still significantly related to the cognitive outcome explaining an extra 9.6% of MMSE and 25.6% of the Clinical Dementia Rating scores variability. Our data suggest that neocortical dendritic spine loss is an independent parameter to consider in AD clinicopathologic correlations.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declare an actual or potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg Z Psychiat Grenzgeb. 1907;64:146–148.
-
- Bouras C, Kövari E, Herrmann FR, Rivara CB, Bailey TL, von Gunten A, Hof PR, Giannakopoulos P. Stereologic analysis of microvascular morphology in the elderly: Alzheimer disease pathology and cognitive status. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65:235–244. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
-
- Bussière T, Friend PD, Sadeghi N, Wicinski B, Lin GI, Bouras C, Giannakopoulos P, Robakis NK, Morrison JH, Perl DP, Hof PR. Stereologic assessment of the total cortical volume occupied by amyloid deposits and its relationship with cognitive status in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience. 2002;112:75–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

