IgG1 B cell receptor signaling is inhibited by CD22 and promotes the development of B cells whose survival is less dependent on Ig alpha/beta
- PMID: 17420268
- PMCID: PMC2118546
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062024
IgG1 B cell receptor signaling is inhibited by CD22 and promotes the development of B cells whose survival is less dependent on Ig alpha/beta
Abstract
We describe a mouse strain in which B cell development relies either on the expression of membrane-bound immunoglobulin (Ig) gamma1 or mu heavy chains. Progenitor cells expressing gamma1 chains from the beginning generate a peripheral B cell compartment of normal size with all subsets, but a partial block is seen at the pro- to pre-B cell transition. Accordingly, gamma1-driven B cell development is disfavored in competition with developing B cells expressing a wild-type (WT) IgH locus. However, the mutant B cells display a long half-life and accumulate in the mature B cell compartment, and even though partial truncation of the Ig alpha cytoplasmic tail compromises their development, it does not affect their maintenance, as it does in WT cells. IgG1-expressing B cells showed an enhanced Ca(2+) response upon B cell receptor cross-linking, which was not due to a lack of inhibition by CD22. The enhanced Ca(2+) response was also observed in mature B cells that had been switched from IgM to IgG1 expression in vivo. Collectively, these results suggest that the gamma1 chain can exert a unique signaling function that can partially replace that of the Ig alpha/beta heterodimer in B cell maintenance and may contribute to memory B cell physiology.
Figures

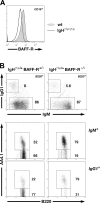


References
-
- Reth, M. 1994. B cell antigen receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 6:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Neuberger, M.S., H.M. Caskey, S. Pettersson, G.T. Williams, and M.A. Surani. 1989. Isotype exclusion and transgene down-regulation in immunoglobulin-lambda transgenic mice. Nature. 338:350–352. - PubMed
-
- Achatz, G., L. Nitschke, and M.C. Lamers. 1997. Effect of transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of IgE on the IgE response. Science. 276:409–411. - PubMed
-
- Kaisho, T., F. Schwenk, and K. Rajewsky. 1997. The roles of gamma 1 heavy chain membrane expression and cytoplasmic tail in IgG1 responses. Science. 276:412–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

