Cellular immune responses in acute hepatitis E virus infection to the viral open reading frame 2 protein
- PMID: 17425421
- PMCID: PMC2443386
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2006.0053
Cellular immune responses in acute hepatitis E virus infection to the viral open reading frame 2 protein
Abstract
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) causes acute viral hepatitis and is endemic in the developing world. Few data are available on cellular immune responses in HEV infection. Using flow cytometry, we studied the frequencies of peripheral blood CD4(+) /CD8(+) T cells secreting interferon (IFN)-gamma, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and interleukin (IL)-4 in 21 patients with acute hepatitis E and 18 healthy controls, after stimulation with the HEV capsid (ORF2) protein. Cytokine levels in serum specimens and culture supernatants of ORF2-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were estimated in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. In addition, cytokine mRNA transcripts were measured in PBMCs by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. In patients with acute hepatitis E, although the total CD4(+) population was expanded, the proportions of CD4(+)/CD69(+) and CD8(+) /CD69(+) cells producing IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and IL-4 in response to HEV ORF2 stimulation were unchanged. However, IFN-gamma levels in the supernatants and IFN-gamma mRNA transcripts in cells were elevated in ORF2-stimulated PBMCs in acute hepatitis E; levels of IL-2 or TNF-alpha were unchanged. Our findings suggest that CD4(+) IFN-gamma-secreting cells, which do not belong either to the helper T cell type 1 or type 2 phenotype, as is the case with natural killer T cells, may be involved in the pathogenesis of hepatitis E. Further, the limited immune reactivity we detected in peripheral blood cells may be related to the sequestration of immune events to the intrahepatic compartment, which is the major disease site.
Figures
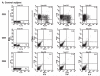


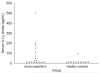
Similar articles
-
Effector T cells immune reactivity among patients with acute hepatitis E.J Viral Hepat. 2011 Oct;18(10):e603-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01489.x. Epub 2011 Jul 12. J Viral Hepat. 2011. PMID: 21914082
-
Cytokine profiles, CTL response and T cell frequencies in the peripheral blood of acute patients and individuals recovered from hepatitis E infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031822. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384080 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis E virus ORF 1 induces proliferative and functional T-cell responses in patients with ongoing and resolved hepatitis E.Liver Int. 2018 Feb;38(2):266-277. doi: 10.1111/liv.13521. Epub 2017 Aug 20. Liver Int. 2018. PMID: 28718943
-
Immunobiology and Host Response to HEV.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;948:113-141. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-0942-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27738982 Review.
-
Increased interleukin-32, interleukin-1, and interferon-γ levels in serum from hepatitis B patients and in HBV-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy volunteers.J Infect Public Health. 2019 Jan-Feb;12(1):7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jul 10. J Infect Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30006119 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-epitope vaccine design for hepatitis E virus based on protein ORF2 and ORF3.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1372069. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1372069. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38577684 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and immune response to hepatitis E viral infection among acute hepatitis patients in Assiut, Egypt.Egypt J Immunol. 2010;17(1):73-86. Egypt J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 22053611 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral T regulatory cells and cytokines in hepatitis E infection.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012 Feb;31(2):179-84. doi: 10.1007/s10096-011-1291-1. Epub 2011 May 20. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 21598072
-
Codon-Optimized Expression and Purification of Truncated ORF2 Protein of Hepatitis E Virus in Escherichia coli.Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014 Jul;7(7):e11261. doi: 10.5812/jjm.11261. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25368796 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Humoral Immune Profiles After Hepatitis E Vaccination and Infection.Viruses. 2025 Jun 26;17(7):901. doi: 10.3390/v17070901. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal R, Krawczynski K. Hepatitis E: An overview and recent advances in clinical and laboratory research. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15:9–20. - PubMed
-
- Arora NK, Nanda SK, Gulati S, Ansari IH, Chawla YK, Gupta SD, Panda SK. Acute viral hepatitis types E, A, and B singly and in combination in acute liver failure in children in north India. J Med Virol. 1996;48:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Bradley DW, Krawczynski K, Cook EH, Jr, McCaustland KA, Humphrey CD, Spelbring JE, Myint H, Maynard JE. Enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis: Serial passage of disease in cynomolgus macaques and tamarins and recovery of disease-associated 27- to 34-nm viruslike particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:6277–6281. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doherty DG, O’Farrelley C. Lymphoid repertoires in healthy liver. In: Gershwin ME, Vierling JM, Manns MN, editors. Liver Immunology. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus; 2003. pp. 31–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

