Cellular immune responses in acute hepatitis E virus infection to the viral open reading frame 2 protein
- PMID: 17425421
- PMCID: PMC2443386
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2006.0053
Cellular immune responses in acute hepatitis E virus infection to the viral open reading frame 2 protein
Abstract
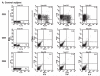
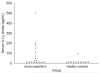
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) causes acute viral hepatitis and is endemic in the developing world. Few data are available on cellular immune responses in HEV infection. Using flow cytometry, we studied the frequencies of peripheral blood CD4(+) /CD8(+) T cells secreting interferon (IFN)-gamma, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and interleukin (IL)-4 in 21 patients with acute hepatitis E and 18 healthy controls, after stimulation with the HEV capsid (ORF2) protein. Cytokine levels in serum specimens and culture supernatants of ORF2-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were estimated in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. In addition, cytokine mRNA transcripts were measured in PBMCs by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. In patients with acute hepatitis E, although the total CD4(+) population was expanded, the proportions of CD4(+)/CD69(+) and CD8(+) /CD69(+) cells producing IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and IL-4 in response to HEV ORF2 stimulation were unchanged. However, IFN-gamma levels in the supernatants and IFN-gamma mRNA transcripts in cells were elevated in ORF2-stimulated PBMCs in acute hepatitis E; levels of IL-2 or TNF-alpha were unchanged. Our findings suggest that CD4(+) IFN-gamma-secreting cells, which do not belong either to the helper T cell type 1 or type 2 phenotype, as is the case with natural killer T cells, may be involved in the pathogenesis of hepatitis E. Further, the limited immune reactivity we detected in peripheral blood cells may be related to the sequestration of immune events to the intrahepatic compartment, which is the major disease site.
Figures


References
-
- Aggarwal R, Krawczynski K. Hepatitis E: An overview and recent advances in clinical and laboratory research. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15:9–20. - PubMed
-
- Arora NK, Nanda SK, Gulati S, Ansari IH, Chawla YK, Gupta SD, Panda SK. Acute viral hepatitis types E, A, and B singly and in combination in acute liver failure in children in north India. J Med Virol. 1996;48:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Bradley DW, Krawczynski K, Cook EH, Jr, McCaustland KA, Humphrey CD, Spelbring JE, Myint H, Maynard JE. Enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis: Serial passage of disease in cynomolgus macaques and tamarins and recovery of disease-associated 27- to 34-nm viruslike particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:6277–6281. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doherty DG, O’Farrelley C. Lymphoid repertoires in healthy liver. In: Gershwin ME, Vierling JM, Manns MN, editors. Liver Immunology. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus; 2003. pp. 31–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

