Cytokines, inflammation, and pain
- PMID: 17426506
- PMCID: PMC2785020
- DOI: 10.1097/AIA.0b013e318034194e
Cytokines, inflammation, and pain
Abstract
Cytokines are small secreted proteins released by cells have a specific effect on the interactions and communications between cells. Cytokine is a general name; other names include lymphokine (cytokines made by lymphocytes), monokine (cytokines made by monocytes), chemokine (cytokines with chemotactic activities), and interleukin (cytokines made by one leukocyte and acting on other leukocytes). Cytokines may act on the cells that secrete them (autocrine action), on nearby cells (paracrine action), or in some instances on distant cells (endocrine action). There are both pro-inflammatory cytokines and anti-inflammatory cytokines. There is significant evidence showing that certain cytokines/chemokines are involved in not only the initiation but also the persistence of pathologic pain by directly activating nociceptive sensory neurons. Certain inflammatory cytokines are also involved in nerve-injury/inflammation-induced central sensitization, and are related to the development of contralateral hyperalgesia/allodynia. The discussion presented in this chapter describes several key pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines and anti-inflammatory cytokines, their relation with pathological pain in animals and human patients, and possible underlying mechanisms.
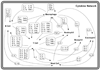
Figures
References
-
- Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF. Glial proinflammatory cytokines mediate exaggerated pain states: implications for clinical pain. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;521:1–21. - PubMed
-
- DeLeo JA, Colburn RW, Nichols M, et al. Interleukin-6-mediated hyperalgesia/allodynia and increased spinal IL-6 expression in a rat mononeuropathy model. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1996;16:695–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

