WTH3 is a direct target of the p53 protein
- PMID: 17426708
- PMCID: PMC2359938
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603724
WTH3 is a direct target of the p53 protein
Abstract
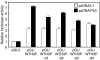
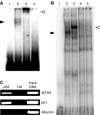
Previous results showed that overexpression of the WTH3 gene in multidrug resistance (MDR) cells reduced MDR1 gene expression and converted their resistance to sensitivity to various anticancer drugs. The WTH3 gene promoter was found to be differentially regulated in paired MDR vs non-MDR MCF7 cells owing to epigenetic modifications and transcription factor modulations. To understand further the mechanisms that govern WTH3's differential expression, we uncovered a p53-binding site in its promoter, which indicated that WTH3 could be regulated by the p53 gene. This hypothesis was then tested by different strategies. The resulting data revealed that (1) the WTH3 promoter was upregulated by the p53 transgene in diverse host cells; (2) there was a correlation between WTH3 expression levels and p53 gene status in a cell line panel; (3) a WTH3 promoter region was directly targeted by the p53 protein in vitro and in vivo. In addition, overexpression of the WTH3 gene promoted the apoptotic phenotype in host cells. On the basis of these findings, we believe that the negative role played by the WTH3 gene in MDR development is through its proapoptotic potential that is regulated by multiple mechanisms at the transcription level, and one of these mechanisms is linked to the p53 gene.
Figures




References
-
- Aas T, Borresen AL, Geisler S, Smith-Sorensen B, Johnsen H, Varhaug JE, Akslen LA, Lonning PE (1996) Specific P53 mutations are associated with de novo resistance to doxorubicin in breast cancer patients. Nat Med 2: 811–814 - PubMed
-
- Adachi K, Toyota M, Sasaki Y, Yamashita T, Ishida S, Ohe-Toyota M, Maruyama R, Hinoda Y, Saito T, Imai K, Kudo R, Tokino T (2004) Identification of SCN3B as a novel p53-inducible proapoptotic gene. Oncogene 23: 7791–7798 - PubMed
-
- Antequera F, Bird A (1993a) CpG islands. Exs 64: 169–185 - PubMed
-
- Barbacid M (1987) ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem 56: 779–827 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

