Determination of pain and response to methylprednisolone in Guillain-Barré syndrome
- PMID: 17426908
- PMCID: PMC2778673
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-006-0515-2
Determination of pain and response to methylprednisolone in Guillain-Barré syndrome
Abstract
Pain can be a serious problem in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Different pain symptoms and the effect of methylprednisolone on pain are evaluated.
Methods: GBS patients were recruited from a randomized placebo-controlled study comparing intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) + methylprednisolone (500 mg for 5 days) versus IVIg + placebo. Presence and severity of pain were prospectively scored at randomization and after 4 weeks. Efficacy of methylprednisolone was evaluated using endpoints: percentage of patients with pain and percentage of patients improving in pain-severity level. Medical records of the subgroup of patients treated in the Erasmus MC were screened retrospectively for different pain symptoms and course. Pain was scored at different time intervals: within 4 weeks before randomization and 0-2, 2-4, 4-24, 24-52 weeks after randomization.
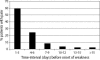
Results: 123 (55%) of 223 patients had pain at randomization. In 70%, pain already started before onset of weakness. Methylprednisolone did not show a positive effect on the presence and reduction of pain. In the subgroup of 39 patients, backache (33%), interscapular (28%), muscle (24%), radicular pain (18%) and painful par-/dysaesthesiae (18%) were most frequently present within the period of 4 weeks before randomization. Twenty-six percent had extreme pain 0-2 weeks after randomization. Most symptoms of pain decreased after this period, but painful par-/dysaesthesiae and muscle pain often remained present during at least 6 months.
Conclusions: Pain frequently occurs, often starts before onset of weakness and may cause severe complaints. Especially painful par-/dysaesthesiae and muscle pain may persist for months. Methylprednisolone seems to have no significant effect on the presence and intensity of pain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of methylprednisolone when added to standard treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin for Guillain-Barré syndrome: randomised trial.Lancet. 2004 Jan 17;363(9404):192-6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(03)15324-x. Lancet. 2004. PMID: 14738791 Clinical Trial.
-
Second IVIg course in Guillain-Barré syndrome patients with poor prognosis (SID-GBS trial): Protocol for a double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial.J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2018 Dec;23(4):210-215. doi: 10.1111/jns.12286. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2018. PMID: 30151941
-
[Contribution of corticosteroid to the treatment of pain in the acute phase of Guillain-Barré syndrome].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2004 Sep;160(8-9):821-3. doi: 10.1016/s0035-3787(04)71037-1. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2004. PMID: 15454869 French.
-
CMV-associated axonal sensory-motor Guillain-Barré syndrome in a child: Case report and review of the literature.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2016 Jan;20(1):168-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2015.11.004. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26621312 Review.
-
European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on diagnosis and treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome.J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2023 Dec;28(4):535-563. doi: 10.1111/jns.12594. Epub 2023 Oct 10. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2023. PMID: 37814551 Review.
Cited by
-
Pain determinants and quality of life in Guillain-Barre syndrome: a prospective cohort study.BMJ Neurol Open. 2024 Dec 11;6(2):e000925. doi: 10.1136/bmjno-2024-000925. eCollection 2024. BMJ Neurol Open. 2024. PMID: 39687605 Free PMC article.
-
Inpatient management of guillain-barré syndrome.Neurohospitalist. 2011 Apr;1(2):78-84. doi: 10.1177/1941875210396379. Neurohospitalist. 2011. PMID: 23983841 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroids for Guillain-Barré syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 24;10(10):CD001446. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001446.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27775812 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatment for pain in Guillain-Barré syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 9;2015(4):CD009950. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009950.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25855461 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and treatment of immune-mediated neuropathies.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2009 Jul;2(4):261-81. doi: 10.1177/1756285609104792. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2009. PMID: 21179533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb04522.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb04522.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7136494', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7136494/'}]}
- Andersson T, Sidén Å (1982) A clinical study of the Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand 66:316–327 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10953191', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10953191/'}]}
- Berciano J, Garćia A, Figols J, Munoz R, Berciano MT, Lafarga M (2000) Perineurium contributes to axonal damage in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 55:552–559 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/bmj.293.6542.325', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.293.6542.325'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1340999', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1340999/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2942218', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2942218/'}]}
- Clague JE, Macmillan RR (1986) Backache and the Guillain-Barré syndrome: a diagnostic problem. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 293:325–326 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00000542-199002000-00026', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199002000-00026'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2301769', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2301769/'}]}
- Connelly M, Shagrin J, Warfield C (1990) Epidural opioids for the management of pain in a patient with the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Anesthesiology 72:381–383 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0022-510X(91)90303-O', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510x(91)90303-o'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1940970', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1940970/'}]}
- de Jager AE, Sluiter HJ (1991) Clinical signs in severe Guillain-Barré syndrome: analysis of 63 patients. J Neurol Sci 104:143–150 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

