Mutation screening of the PTEN gene in patients with autism spectrum disorders and macrocephaly
- PMID: 17427195
- PMCID: PMC3381648
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30493
Mutation screening of the PTEN gene in patients with autism spectrum disorders and macrocephaly
Abstract
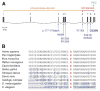
Mutations in the PTEN gene are associated with a broad spectrum of disorders, including Cowden syndrome (CS), Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome, Proteus syndrome, and Lhermitte-Duclos disease. In addition, PTEN mutations have been described in a few patients with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and macrocephaly. In this study, we screened the PTEN gene for mutations and deletions in 88 patients with ASDs and macrocephaly (defined as >or=2 SD above the mean). Mutation analysis was performed by direct sequencing of all exons and flanking regions, as well as the promoter region. Dosage analysis of PTEN was carried out using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). No partial or whole gene deletions were observed. We identified a de novo missense mutation (D326N) in a highly conserved amino acid in a 5-year-old boy with autism, mental retardation, language delay, extreme macrocephaly (+9.6 SD) and polydactyly of both feet. Polydactyly has previously been described in two patients with Lhermitte-Duclos disease and CS and is thus likely to be a rare sign of PTEN mutations. Our findings suggest that PTEN mutations are a relatively infrequent cause of ASDs with macrocephaly. Screening of PTEN mutations is warranted in patients with autism and pronounced macrocephaly, even in the absence of other features of PTEN-related tumor syndromes.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bielschowsky M, Simons A. Über diffuse Hamartome (Ganglioneurome) des Kleinhirns und ihre Genese. J Psychol Neurol. 1930;41:50–75.
-
- Butler MG, Dasouki MJ, Zhou XP, Talebizadeh Z, Brown M, Takahashi TN, Miles JH, Wang CH, Stratton R, Pilarski R, Eng C. Subset of individuals with autism spectrum disorders and extreme macrocephaly associated with germline PTEN tumour suppressor gene mutations. J Med Genet. 2005;42:318–321. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Garelick MG, Wang H, Lil V, Athos J, Storm DR. PI3 kinase signaling is required for retrieval and extinction of contextual memory. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:925–931. - PubMed
-
- Curatolo P, Porfirio MC, Manzi B, Seri S. Autism in tuberous sclerosis. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2004;8:327–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

