A major zebrafish polymorphism resource for genetic mapping
- PMID: 17428331
- PMCID: PMC1896001
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-4-r55
A major zebrafish polymorphism resource for genetic mapping
Abstract
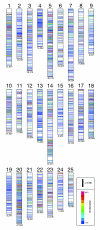
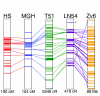
We have identified 645,088 candidate polymorphisms in zebrafish and observe a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) validation rate of 71% to 86%, improving with polymorphism confidence score. Variant sites are non-random, with an excess of specific novel T- and A-rich motifs. We positioned half of the polymorphisms on zebrafish genetic and physical maps as a resource for positional cloning. We further demonstrate bulked segregant analysis using the anchored SNPs as a method for high-throughput genetic mapping in zebrafish.
Figures

References
-
- Driever W, Solnica-Krezel L, Schier AF, Neuhauss SC, Malicki J, Stemple DL, Stainier DY, Zwartkruis F, Abdelilah S, Rangini Z, et al. A genetic screen for mutations affecting embryogenesis in zebrafish. Development. 1996;123:37–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

