The abundant R2 mRNA generated by aleutian mink disease parvovirus is tricistronic, encoding NS2, VP1, and VP2
- PMID: 17428872
- PMCID: PMC1933312
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00244-07
The abundant R2 mRNA generated by aleutian mink disease parvovirus is tricistronic, encoding NS2, VP1, and VP2
Abstract
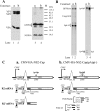
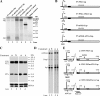
The abundant R2 mRNA encoded by the single left-end promoter of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus is tricistronic; it not only expresses the capsid proteins VP1 and VP2 but is also the major source for the nonstructural protein NS2. A cis-acting sequence within the NS2 gene was shown to be required for efficient capsid protein production, and its effect displayed a distinct location dependence. Ribosome transit through the upstream NS2 gene region was necessary for efficient VP1 and VP2 expression; however, neither ablation nor improvement of the NS2 initiating AUG had an effect on capsid protein production, suggesting that the translation of the NS2 protein per se had little influence on VP1 and VP2 expression. Thus, proper control of the alternative translation of the tricistronic R2 mRNA, a process critical for viral replication, is governed in a complex manner.
Figures

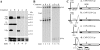
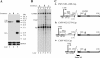

References
-
- Alexandersen, S. 1986. Acute interstitial pneumonia in mink kits: experimental reproduction of the disease. Vet. Pathol. 23:579-588. - PubMed
-
- Alexandersen, S., M. E. Bloom, J. Wolfinbarger, and R. E. Race. 1987. In situ molecular hybridization for detection of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus DNA by using strand-specific probes: identification of target cells for viral replication in cell cultures and in mink kits with virus-induced interstitial pneumonia. J. Virol. 61:2407-2419. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexandersen, S., A. Uttenthal-Jensen, and B. Aasted. 1986. Demonstration of non-degraded Aleutian disease virus (ADV) proteins in lung tissue from experimentally infected mink kits. Arch. Virol. 87:127-133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

