Amygdala neurons differentially encode motivation and reinforcement
- PMID: 17428967
- PMCID: PMC6672525
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5281-06.2007
Amygdala neurons differentially encode motivation and reinforcement
Abstract
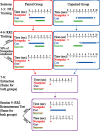
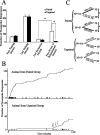
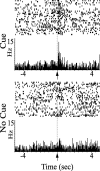
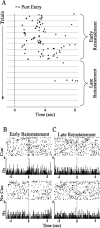
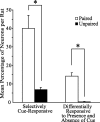
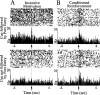
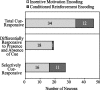
Lesion studies demonstrate that the basolateral amygdala complex (BLA) is important for assigning motivational significance to sensory stimuli, but little is known about how this information is encoded. We used in vivo electrophysiology procedures to investigate how the amygdala encodes motivating and reinforcing properties of cues that induce reinstatement of reward-seeking behavior. Two groups of rats were trained to respond to a sucrose reward. The "paired" group was trained with a reward-predictive cue, whereas the "unpaired" group was trained with a randomly presented cue. Both groups underwent identical extinction and reinstatement procedures during which the reward was withheld. The proportion of neurons that were phasically cue responsive during reinstatement was significantly higher in the paired group (46 of 100) than in the unpaired group (8 of 112). Cues that induce reward-seeking behavior can do so by acting as incentives or reinforcers. Distinct populations of neurons responded to the cue in trials in which the cue acted as an incentive, triggering a motivated reward-seeking state, or as a reinforcer, supporting continued instrumental responding. The incentive motivation-encoding population of neurons (34 of 46 cue-responsive neurons; 74%) extinguished in temporal agreement with a decrease in the rate of instrumental responding. The conditioned reinforcement-encoding population of neurons (12 of 46 cue-responsive neurons; 26%) maintained their response for the duration of cue-reinforced instrumental responding. These data demonstrate that separate populations of cue-responsive neurons in the BLA encode the motivating or reinforcing properties of a cue previously associated with a reward.
Figures

References
-
- Arroyo M, Markou A, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ. Acquisition, maintenance and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration under a second-order schedule of reinforcement in rats: effects of conditioned cues and continuous access to cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1998;140:331–344. - PubMed
-
- Berridge KC, Robinson TE. Parsing reward. Trends Neurosci. 2003;26:507–513. - PubMed
-
- Cador M, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ. Involvement of the amygdala in stimulus-reward associations: interaction with the ventral striatum. Neuroscience. 1989;30:77–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
