Light triggers expression of philanthotoxin-insensitive Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in the developing rat retina
- PMID: 17430992
- PMCID: PMC2075288
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.127894
Light triggers expression of philanthotoxin-insensitive Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in the developing rat retina
Abstract
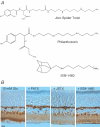
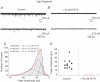
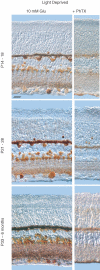
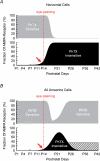
Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors (AMPARs) are expressed throughout the adult CNS but yet their role in development is poorly understood. In the developing retina, most investigations have focused on Ca2+ influx through NMDARs in promoting synapse maturation and not on AMPARs. However, NMDARs are absent from many retinal cells suggesting that other Ca2+-permeable glutamate receptors may be important to consider. Here we show that inhibitory horizontal and AII amacrine cells lack NMDARs but express Ca2+-permeable AMPARs. Before eye-opening, AMPARs were fully blocked by philanthotoxin (PhTX), a selective antagonist of Ca2+-permeable AMPARs. After eye-opening, however, a subpopulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPARs were unexpectedly PhTX resistant. Furthermore, Joro spider toxin (JSTX) and IEM-1460 also failed to antagonize, demonstrating that this novel pharmacology is shared by several AMPAR channel blockers. Interestingly, PhTX-insensitive AMPARs failed to express in retinae from dark-reared animals demonstrating that light entering the eye triggers their expression. Eye-opening coincides with the consolidation of inhibitory cell connections suggesting that the developmental switch to a Ca2+-permeable AMPAR with novel pharmacology may be critical to synapse maturation in the mammalian retina.
Figures







Comment in
-
A light switch controlling Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in the retina.J Physiol. 2007 Jul 1;582(Pt 1):3. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.135145. Epub 2007 Apr 26. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17463033 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aizenman E, Karschin A, Lipton SA. Two pharmacological classes of quisqualate-induced electrical responses in rat retinal ganglion cells in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989;174:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Bellone C, Luscher C. Cocaine triggered AMPA receptor redistribution is reversed in vivo by mGluR-dependent long-term depression. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:636–641. - PubMed
-
- Bowie D, Bähring R, Mayer ML. Block of kainate and AMPA receptors by polyamines and arthropod toxins. In: Jonas P, Monyer H, editors. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors in the CNS. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1999. pp. 251–373.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

