Human prostate epithelium lacks Wee1A-mediated DNA damage-induced checkpoint enforcement
- PMID: 17431037
- PMCID: PMC1855358
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609299104
Human prostate epithelium lacks Wee1A-mediated DNA damage-induced checkpoint enforcement
Abstract
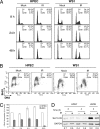
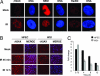
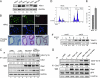
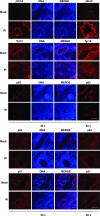
Cellular DNA damage triggers the DNA damage response pathway and leads to enforcement of cell cycle checkpoints, which are essential for the maintenance of genomic integrity and are activated in early stages of tumorigenesis. A special feature of prostate cancer is its high incidence and multifocality. To address the functionality of DNA damage checkpoints in the prostate, we analyzed the responses of human primary prostate epithelial cells (HPECs) and freshly isolated human prostate tissues to gamma-irradiation. We find that gamma-irradiation activates the ataxia telangiectasia mutated-associated DNA damage response pathway in the HPECs but that the clearance of phosphorylated histone H2AX (gammaH2AX) foci is delayed. Surprisingly, gamma-irradiated HPECs were unable to enforce cell cycle checkpoint arrest and had sustained cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2)-associated kinase activity because of a lack of inhibitory Cdk phosphorylation by Wee1A tyrosine kinase. We further show that HPECs express low levels of Wee1A and that ectopic Wee1A efficiently rescues the checkpoints. We recapitulate the absence of checkpoint responses in epithelium of ex vivo irradiated human prostate tissue despite robust induction of gammaH2AX. The findings show that prostate epithelium has a surprising inability to control checkpoint arrest, the lack of which may predispose to accrual of DNA lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contrasting DNA damage checkpoint responses in epithelium of the human seminal vesicle and prostate.Prostate. 2012 Jul 1;72(10):1060-70. doi: 10.1002/pros.21509. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Prostate. 2012. PMID: 22072329
-
Priming phosphorylation of Chk2 by polo-like kinase 3 (Plk3) mediates its full activation by ATM and a downstream checkpoint in response to DNA damage.Mutat Res. 2006 Apr 11;596(1-2):166-76. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.12.002. Epub 2006 Feb 14. Mutat Res. 2006. PMID: 16481012
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated is not required for p53 induction and apoptosis in irradiated epithelial tissues.Mol Cancer Res. 2007 Dec;5(12):1312-8. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0223. Mol Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 18171989
-
[Cell cycle regulation after exposure to ionizing radiation].Bull Cancer. 1999 Apr;86(4):345-57. Bull Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10341340 Review. French.
-
The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective.Nature. 2000 Nov 23;408(6811):433-9. doi: 10.1038/35044005. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11100718 Review.
Cited by
-
Prostate-targeted radiosensitization via aptamer-shRNA chimeras in human tumor xenografts.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jun;121(6):2383-90. doi: 10.1172/JCI45109. Epub 2011 May 9. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21555850 Free PMC article.
-
Wee1 inhibition by MK-1775 leads to tumor inhibition and enhances efficacy of gemcitabine in human sarcomas.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057523. Epub 2013 Mar 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23520471 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Addressing Patient Specificity in the Engineering of Tumor Models.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Sep 12;7:217. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00217. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31572718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A tissue graft model of DNA damage response in the normal and malignant human prostate.J Urol. 2014 Mar;191(3):842-9. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Urol. 2014. PMID: 24035881 Free PMC article.
-
Differential epithelium DNA damage response to ATM and DNA-PK pathway inhibition in human prostate tissue culture.Cell Cycle. 2011 Oct 15;10(20):3545-53. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.20.17841. Epub 2011 Oct 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 22030624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartwell L. Cell. 1992;71:543–546. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. Cell. 2004;118:9–17. - PubMed
-
- Bartek J, Lukas C, Lukas J. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:792–804. - PubMed
-
- Kastan MB, Bartek J. Nature. 2004;432:316–323. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Horejsi Z, Koed K, Kramer A, Tort F, Zieger K, Guldberg P, Sehested M, Nesland JM, Lukas C, et al. Nature. 2005;434:864–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

