Activation of the alpha7 nAChR reduces acid-induced acute lung injury in mice and rats
- PMID: 17431097
- PMCID: PMC1976545
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0240OC
Activation of the alpha7 nAChR reduces acid-induced acute lung injury in mice and rats
Abstract
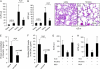
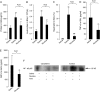
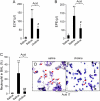
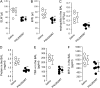
New evidence indicates that neural mechanisms can down-regulate acute inflammation. In these studies, we tested the potential role of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (alpha7 nAChR) in a rodent model of acid-induced acute lung injury. We first determined that the alpha7 nAChR was expressed by alveolar macrophages and lung epithelial cells. Then, using an acid-induced acute lung injury mouse model, we found that nicotine, choline, and PNU-282,987 (a specific alpha7 nAChR agonist) decreased excess lung water and lung vascular permeability, and reduced protein concentration in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). Deficiency of alpha7 nAChR resulted in a 2-fold increase in excess lung water and lung vascular permeability. The reduction of proinflammatory cytokines (macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and TNF-alpha) in the BAL with nicotine probably resulted from the suppression of NF-kappaB activation in alveolar macrophages. The beneficial effect of nicotine was also tested in rat model of acid-induced acute lung injury in which BAL protein and receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), a marker of type I cell injury, were reduced by nicotine treatment. These results indicate that activation of alpha7 nAChR may provide a new therapeutic pathway for the treatment of acute lung injury.
Figures

References
-
- Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000;405:458–462. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang H, Yang H, Ulloa L, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 2003;421:384–388. - PubMed
-
- van Westerloo DJ, Giebelen IA, Florquin S, Daalhuisen J, Bruno MJ, de Vos AF, Tracey KJ, van der Poll T. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway regulates the host response during septic peritonitis. J Infect Dis 2005;191:2138–2148. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Liao H, Ochani M, Justiniani M, Lin X, Yang L, Al-Abed Y, Wang H, Metz C, Miller EJ, et al. Cholinergic agonists inhibit HMGB1 release and improve survival in experimental sepsis. Nat Med 2004;10:1216–1221. - PubMed
-
- Matthay MA, Ware LB. Can nicotine treat sepsis? Nat Med 2004;10:1161–1162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

