Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in a mouse xenograft model with an immunotoxin which is engineered to eliminate vascular leak syndrome
- PMID: 17431617
- PMCID: PMC11030707
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-007-0321-4
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in a mouse xenograft model with an immunotoxin which is engineered to eliminate vascular leak syndrome
Abstract
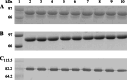
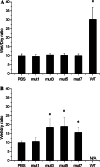
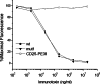
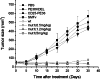
Vascular leak syndrome (VLS) is the major dose-limiting toxicity of immunotoxin and interleukin-2 therapy. It has been evidenced that VLS-inducing molecules share a three-amino acid consensus motif, (x)D(y), which may be responsible for initiating VLS. Here we have constructed a recombinant immunotoxin (SMFv-PE38KDEL) by genetically fusing PE38KDEL to a single-chain antibody derived from SM5-1 monoclonal antibody, which has a high specificity for melanoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and breast cancer. In order to eliminate VLS induced by this PE38KDEL-based immunotoxin, a panel of mutants were generated by changing amino acid residues adjacent to its three (x)D(y) motifs in the three-dimensional structure. One of the SMFv-PE38KDEL mutants, denoted as mut1, displayed a similar protein synthesis inhibitory in a reticulocyte lysate translation assay compared to the wild-type SMFv-PE38KDEL (wt). The in vitro cytotoxicity assay indicated that mut1 specifically killed SM5-1 binding protein-positive tumor cells, although its cytotoxicity was slightly less than wt. In contrast, mut1 was shown to be much weaker in inducing VLS in mice than wt. The LD(50) values of wt and mut1 in mice were investigated with the result that the LD(50) of mut1 was about tenfold higher than that of wt. The in vivo antitumor activity of wt and mut1 were also compared in tumor-bearing nude mice. Both wt and mut1 were effective in inhibiting the tumor growth but mut1 showed improved therapeutic efficacy. These studies suggest mut1 may be a novel PE-based immunotoxin with much less toxicity for clinical use.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice with PE38KDEL type I mutant-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles conjugated with humanized SM5-1 F(ab') fragments.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Oct;7(10):3399-407. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0514. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18852143
-
Expression, purification, and characterization of an immunotoxin containing a humanized anti-CD25 single-chain fragment variable antibody fused to a modified truncated Pseudomonas exotoxin A.Protein Expr Purif. 2008 Mar;58(1):140-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2007.09.009. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Protein Expr Purif. 2008. PMID: 17950620
-
Preparation and characterization of PE38KDEL-loaded anti-HER2 nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy.J Control Release. 2008 Jun 24;128(3):209-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.03.010. Epub 2008 Mar 19. J Control Release. 2008. PMID: 18450313
-
Immunotoxins constructed with chimeric, short-lived anti-CD22 monoclonal antibodies induce less vascular leak without loss of cytotoxicity.MAbs. 2012 Jan-Feb;4(1):57-68. doi: 10.4161/mabs.4.1.18348. MAbs. 2012. PMID: 22327430 Free PMC article.
-
Construction, expression, and characterization of an anti-tumor immunotoxin containing the human anti-c-Met single-chain antibody and PE38KDEL.Immunol Lett. 2013 Jan;149(1-2):30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Immunol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23026237
Cited by
-
Disorders of Vascular Permeability.Annu Rev Pathol. 2016 May 23;11:251-81. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012615-044506. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Annu Rev Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26907525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a re-engineered, mesothelin-targeted Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion protein for lung cancer therapy.Mol Oncol. 2016 Oct;10(8):1317-29. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Mol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27507537 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions Between Pseudomonas Immunotoxins and the Plasma Membrane: Implications for CAT-8015 Immunotoxin Therapy.Front Oncol. 2018 Nov 27;8:553. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00553. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30538953 Free PMC article.
-
An immunotoxin targeting Ebola virus glycoprotein inhibits Ebola virus production from infected cells.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 7;16(1):e0245024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245024. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33411835 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-DR5 monoclonal antibody-mediated DTIC-loaded nanoparticles combining chemotherapy and immunotherapy for malignant melanoma: target formulation development and in vitro anticancer activity.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:1991-2005. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S24094. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011. PMID: 21976975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vitetta ES. Immunotoxins and vascular leak syndrome. Cancer J Suppl. 2000;3:S218–S224. - PubMed
-
- Wels W, Harwerth IM, Hynes NE, Groner B. Diminution of antibodies directed against tumor cell surface epitopes: a single chain Fv fusion molecule specifically recognizes the extracellular domain of the c-erbB-2 receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;43:1–7. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90180-Q. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

