The sodium channel Nav1.5a is the predominant isoform expressed in adult mouse dorsal root ganglia and exhibits distinct inactivation properties from the full-length Nav1.5 channel
- PMID: 17433712
- PMCID: PMC2726334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.03.002
The sodium channel Nav1.5a is the predominant isoform expressed in adult mouse dorsal root ganglia and exhibits distinct inactivation properties from the full-length Nav1.5 channel
Abstract
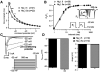
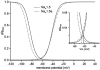
Nav1.5 is the principal voltage-gated sodium channel expressed in heart, and is also expressed at lower abundance in embryonic dorsal root ganglia (DRG) with little or no expression reported postnatally. We report here the expression of Nav1.5 mRNA isoforms in adult mouse and rat DRG. The major isoform of mouse DRG is Nav1.5a, which encodes a protein with an IDII/III cytoplasmic loop reduced by 53 amino acids. Western blot analysis of adult mouse DRG membrane proteins confirmed the expression of Nav1.5 protein. The Na+ current produced by the Nav1.5a isoform has a voltage-dependent inactivation significantly shifted to more negative potentials (by approximately 5 mV) compared to the full-length Nav1.5 when expressed in the DRG neuroblastoma cell line ND7/23. These results imply that the alternatively spliced exon 18 of Nav1.5 plays a role in channel inactivation and that Nav1.5a is likely to make a significant contribution to adult DRG neuronal function.
Figures
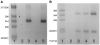
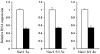
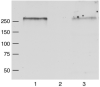
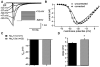
Similar articles
-
Heterologous expression and functional analysis of rat Nav1.8 (SNS) voltage-gated sodium channels in the dorsal root ganglion neuroblastoma cell line ND7-23.Neuropharmacology. 2004 Mar;46(3):425-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.09.018. Neuropharmacology. 2004. PMID: 14975698
-
Nav1.3 sodium channels: rapid repriming and slow closed-state inactivation display quantitative differences after expression in a mammalian cell line and in spinal sensory neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 15;21(16):5952-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-05952.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11487618 Free PMC article.
-
Contactin regulates the current density and axonal expression of tetrodotoxin-resistant but not tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in DRG neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jul;22(1):39-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04186.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16029194
-
The neuroleptic drug, fluphenazine, blocks neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels.Brain Res. 2006 Aug 23;1106(1):72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.05.076. Epub 2006 Jul 12. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16839522
-
Novel isoforms of the sodium channels Nav1.8 and Nav1.5 are produced by a conserved mechanism in mouse and rat.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jun 4;279(23):24826-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401281200. Epub 2004 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15047701 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Distribution and function of voltage-gated sodium channels in the nervous system.Channels (Austin). 2017 Nov 2;11(6):534-554. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2017.1380758. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Channels (Austin). 2017. PMID: 28922053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium Channel Nav1.8 Underlies TTX-Resistant Axonal Action Potential Conduction in Somatosensory C-Fibers of Distal Cutaneous Nerves.J Neurosci. 2017 May 17;37(20):5204-5214. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3799-16.2017. Epub 2017 Apr 27. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28450535 Free PMC article.
-
Pyramidal cells of rodent presubiculum express a tetrodotoxin-insensitive Na+ current.J Physiol. 2009 Sep 1;587(Pt 17):4249-64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.175349. Epub 2009 Jul 13. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19596892 Free PMC article.
-
NaV1.5 sodium channel window currents contribute to spontaneous firing in olfactory sensory neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2014 Sep 1;112(5):1091-104. doi: 10.1152/jn.00154.2014. Epub 2014 May 28. J Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24872539 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mRNA isoforms of the sodium channels Na(v)1.2, Na(v)1.3 and Na(v)1.7 encode predicted two-domain, truncated proteins.Neuroscience. 2008 Aug 26;155(3):797-808. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.04.060. Epub 2008 May 6. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18675520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Wood JN. A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature. 1996;379:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 1999;2:541–548. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Dib-Hajj S, Cohen S, Hinson AW, Waxman SG. Glial cells have heart: rH1 Na+ channel mRNA and protein in spinal cord astrocytes. Glia. 1998;23:200–208. - PubMed
-
- Choi JS, Tyrrell L, Waxman SG, Dib-Hajj SD. Functional role of the C-terminus of voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.8. FEBS Lett. 2004;572:256–260. - PubMed
-
- Cohen SA, Levitt LK. Partial characterization of the rH1 sodium channel protein from rat heart using subtype-specific antibodies. Circ. Res. 1993;73:735–742. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

