Joint estimates of quantitative trait locus effect and frequency using synthetic recombinant populations of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 17435224
- PMCID: PMC1894589
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.069641
Joint estimates of quantitative trait locus effect and frequency using synthetic recombinant populations of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
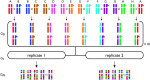
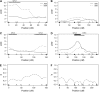
We develop and implement a strategy to map QTL in two synthetic populations of Drosophila melanogaster each initiated with eight inbred founder strains. These recombinant populations allow simultaneous estimates of QTL location, effect, and frequency. Five X-linked QTL influencing bristle number were resolved to intervals of approximately 1.3 cM. We confirm previous observations of bristle number QTL distal to 4A at the tip of the chromosome and identify two novel QTL in 7F-8C, an interval that does not include any classic bristle number candidate genes. If QTL at the tip of the X are biallelic they appear to be intermediate in frequency, although there is evidence that these QTL may reside in multiallelic haplotypes. Conversely, the two QTL mapping to the middle of the X chromosome are likely rare: in each case the minor allele is observed in only 1 of the 16 founders. Assuming additivity and biallelism we estimate that identified QTL contribute 1.0 and 8.7%, respectively, to total phenotypic variation in male abdominal and sternopleural bristle number in nature. Models that seek to explain the maintenance of genetic variation make different predictions about the population frequency of QTL alleles. Thus, mapping QTL in eight-way recombinant populations can distinguish between these models.
Figures




References
-
- Adams, M. D., S. E. Celniker, R. A. Holt, C. A. Evans, J. D. Gocayne et al., 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287 2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S., M. D. Rand and R. J. Lake, 1999. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284 770–776. - PubMed
-
- Barton, N. H., and M. Turelli, 1989. Evolutionary quantitative genetics: How little do we know? Annu. Rev. Genet. 23 337–370. - PubMed
-
- Barton, N. H., and P. D. Keightley, 2002. Understanding quantitative genetic variation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3 11–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

