Isolated hepatitis B core antibody is associated with HIV and ongoing but not resolved hepatitis C virus infection in a cohort of US women
- PMID: 17436223
- PMCID: PMC3133731
- DOI: 10.1086/515578
Isolated hepatitis B core antibody is associated with HIV and ongoing but not resolved hepatitis C virus infection in a cohort of US women
Abstract
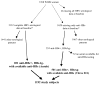
To characterize predictors of isolated hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) among human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected and HIV-uninfected women, we compared 702 women with anti-HBc and hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs) with 490 women with isolated anti-HBc (1.8% of whom had detectable hepatitis B virus [HBV] DNA). Factors independently associated with isolated anti-HBc without viremia were detectable hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA, HIV positivity, history of injection drug use, >10 lifetime sex partners, and HIV RNA level >100,000 copies/mL. Anti-HBs levels were lower among anti-HCV-positive women. Isolated anti-HBc was rarely explained by occult HBV in this cohort but may be explained by the influence of viral coinfections on anti-HBs level or durability.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: none reported.
Figures
References
-
- Neau D, Winnock M, Galperinep T, et al. Isolated antibodies against the core antigen of hepatitis B virus in HIV-infected patients. HIV Med. 2004;5:171–3. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi RT, Wurcel A, Lee H. Isolated antibody to hepatitis B core antigen in HIV-infected individuals. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1602–5. - PubMed
-
- Jilg W, Sieger E, Zachoval R, Schatzl H. Individual with antibodies against hepatitis B core antigen: high percentage of carriers of hepatitis B and C virus. J Hepatol. 1995;23:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Greub G, Frei PC. Isolated antibody to hepatitis B core is associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2000;6:629. - PubMed
-
- Berger A, Doerr HW, Rabenau HF, Weber B. High frequency of HCV infection in individuals with isolated antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. Intervirology. 2000;43:71–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-33834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057006/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-34994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-34993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-26743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-057006/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-42590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CH-32632/CH/OID CDC HHS/United States
- M01 RR000071/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00071/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-34989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

