Oral decontamination with chlorhexidine reduces the incidence of nosocomial pneumonia
- PMID: 17437650
- PMCID: PMC2151882
- DOI: 10.1186/cc5129
Oral decontamination with chlorhexidine reduces the incidence of nosocomial pneumonia
Figures
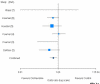
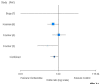
Comment on
-
Effect of oral decontamination with chlorhexidine on the incidence of nosocomial pneumonia: a meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2006 Feb;10(1):R35. doi: 10.1186/cc4837. Crit Care. 2006. PMID: 16507165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeRiso A, Ladowski J, Dillon T, Justice J, Peterson A. Chlorhexidine gluconate 0.12% oral rinse reduces the incidence of total nosocomial respiratory infection and nonprophylactic systemic antibiotic use in patients undergoing heart surgery. Chest. 1996;109:1556–1561. - PubMed
-
- Fourrier F, Dubois D, Pronnier P, Herbecq P, Leroy O, Desmettre T, Pottier-Cau E, Boutigny H, Di Pompeo C, Durocher A, Roussel-Delvallez M, for the PIRAD Study Group Effect of gingival and dental plaque antiseptic decontamination on nosocomial infections acquired in the intensive care unit: a double-blind placebo controlled multicenter study. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:1728–1735. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000171537.03493.B0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Houston S, Hougland P, Anderson J, LaRocco M, Kennedy V, Gentry L. Effectiveness of 0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse in reducing prevalence of nosocomial pneumonia in patients undergoing heart surgery. Am J Crit Care. 2002;11:567–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

