The tumor suppressor microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene
- PMID: 17437991
- PMCID: PMC1855228
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1540407
The tumor suppressor microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene
Abstract
HMGA2, a high-mobility group protein, is oncogenic in a variety of tumors, including benign mesenchymal tumors and lung cancers. Knockdown of Dicer in HeLa cells revealed that the HMGA2 gene is transcriptionally active, but its mRNA is destabilized in the cytoplasm through the microRNA (miRNA) pathway. HMGA2 was derepressed upon inhibition of let-7 in cells with high levels of the miRNA. Ectopic expression of let-7 reduced HMGA2 and cell proliferation in a lung cancer cell. The effect of let-7 on HMGA2 was dependent on multiple target sites in the 3' untranslated region (UTR), and the growth-suppressive effect of let-7 on lung cancer cells was rescued by overexpression of the HMGA2 ORF without a 3'UTR. Our results provide a novel example of suppression of an oncogene by a tumor-suppressive miRNA and suggest that some tumors activate the oncogene through chromosomal translocations that eliminate the oncogene's 3'UTR with the let-7 target sites.
Figures
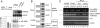


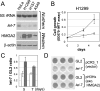
Comment in
-
Oncogenic HMGA2: short or small?Genes Dev. 2007 May 1;21(9):1005-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.1554707. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17473167 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ashar H.R., Tkachenko A., Shah P., Chada K., Tkachenko A., Shah P., Chada K., Shah P., Chada K., Chada K. HMGA2 is expressed in an allele-specific manner in human lipomas. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2003;143:160–168. - PubMed
-
- Ayoubi T.A., Jansen E., Meulemans S.M., de Van Ven W.J., Jansen E., Meulemans S.M., de Van Ven W.J., Meulemans S.M., de Van Ven W.J., de Van Ven W.J. Regulation of HMGIC expression: An architectural transcription factor involved in growth control and development. Oncogene. 1999;18:5076–5087. - PubMed
-
- Berlingieri M.T., Manfioletti G., Santoro M., Bandiera A., Visconti R., Giancotti V., Fusco A., Manfioletti G., Santoro M., Bandiera A., Visconti R., Giancotti V., Fusco A., Santoro M., Bandiera A., Visconti R., Giancotti V., Fusco A., Bandiera A., Visconti R., Giancotti V., Fusco A., Visconti R., Giancotti V., Fusco A., Giancotti V., Fusco A., Fusco A. Inhibition of HMGI-C protein synthesis suppresses retrovirally induced neoplastic transformation of rat thyroid cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995;15:1545–1553. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berner J.M., Meza-Zepeda L.A., Kools P.F., Forus A., Schoenmakers E.F., de Van Ven W.J., Fodstad O., Myklebost O., Meza-Zepeda L.A., Kools P.F., Forus A., Schoenmakers E.F., de Van Ven W.J., Fodstad O., Myklebost O., Kools P.F., Forus A., Schoenmakers E.F., de Van Ven W.J., Fodstad O., Myklebost O., Forus A., Schoenmakers E.F., de Van Ven W.J., Fodstad O., Myklebost O., Schoenmakers E.F., de Van Ven W.J., Fodstad O., Myklebost O., de Van Ven W.J., Fodstad O., Myklebost O., Fodstad O., Myklebost O., Myklebost O. HMGIC, the gene for an architectural transcription factor, is amplified and rearranged in a subset of human sarcomas. Oncogene. 1997;14:2935–2941. - PubMed
-
- Bol S., Wanschura S., Thode B., Deichert U., de Van Ven W.J., Bartnitzke S., Bullerdiek J., Wanschura S., Thode B., Deichert U., de Van Ven W.J., Bartnitzke S., Bullerdiek J., Thode B., Deichert U., de Van Ven W.J., Bartnitzke S., Bullerdiek J., Deichert U., de Van Ven W.J., Bartnitzke S., Bullerdiek J., de Van Ven W.J., Bartnitzke S., Bullerdiek J., Bartnitzke S., Bullerdiek J., Bullerdiek J. An endometrial polyp with a rearrangement of HMGI-C underlying a complex cytogenetic rearrangement involving chromosomes 2 and 12. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1996;90:88–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
