A signal from inside the peroxisome initiates its division by promoting the remodeling of the peroxisomal membrane
- PMID: 17438077
- PMCID: PMC2064137
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200609072
A signal from inside the peroxisome initiates its division by promoting the remodeling of the peroxisomal membrane
Abstract
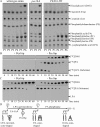
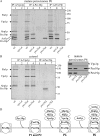
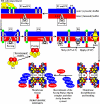
We define the dynamics of spatial and temporal reorganization of the team of proteins and lipids serving peroxisome division. The peroxisome becomes competent for division only after it acquires the complete set of matrix proteins involved in lipid metabolism. Overloading the peroxisome with matrix proteins promotes the relocation of acyl-CoA oxidase (Aox), an enzyme of fatty acid beta-oxidation, from the matrix to the membrane. The binding of Aox to Pex16p, a membrane-associated peroxin required for peroxisome biogenesis, initiates the biosynthesis of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol (DAG) in the membrane. The formation of these two lipids and the subsequent transbilayer movement of DAG initiate the assembly of a complex between the peroxins Pex10p and Pex19p, the dynamin-like GTPase Vps1p, and several actin cytoskeletal proteins on the peroxisomal surface. This protein team promotes membrane fission, thereby executing the terminal step of peroxisome division.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Peroxisome division in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica is regulated by a signal from inside the peroxisome.J Cell Biol. 2003 Sep 29;162(7):1255-66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200305055. Epub 2003 Sep 22. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14504266 Free PMC article.
-
Pex20p functions as the receptor for non-PTS1/non-PTS2 acyl-CoA oxidase import into peroxisomes of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica.Traffic. 2019 Jul;20(7):504-515. doi: 10.1111/tra.12652. Epub 2019 May 27. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 31042004
-
Peroxisome biogenesis disorders: molecular basis for impaired peroxisomal membrane assembly: in metabolic functions and biogenesis of peroxisomes in health and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1822(9):1337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22705440 Review.
-
Yarrowia lipolytica cells mutant for the peroxisomal peroxin Pex19p contain structures resembling wild-type peroxisomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Nov;12(11):3353-64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.11.3353. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11694572 Free PMC article.
-
De novo peroxisome biogenesis: Evolving concepts and conundrums.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1863(5):892-901. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.014. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26381541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of Peroxisome Membrane Dynamics.Front Physiol. 2022 Feb 3;13:834411. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.834411. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35185625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid peroxisomal responses to ROS suggest an alternative mechanistic model for post-biogenesis peroxisomal life cycle in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Aug;4(8):787-9. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.8.9232. Epub 2009 Aug 8. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19820326 Free PMC article.
-
Geometric instability catalyzes mitochondrial fission.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Jan 1;30(1):160-168. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-01-0018. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30379601 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome biogenesis, membrane contact sites, and quality control.EMBO Rep. 2019 Jan;20(1):e46864. doi: 10.15252/embr.201846864. Epub 2018 Dec 10. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 30530632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisomes take shape.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Dec;14(12):803-17. doi: 10.1038/nrm3700. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24263361 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Athenstaedt, K., and G. Daum. 1999. Phosphatidic acid, a key intermediate in lipid metabolism. Eur. J. Biochem. 266:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Bankaitis, V.A. 2002. Slick recruitment to the Golgi. Science. 295:290–291. - PubMed
-
- Behnia, R., and S. Munro. 2005. Organelle identity and the signposts for membrane traffic. Nature. 438:597–604. - PubMed
-
- Boukh-Viner, T., T. Guo, A. Alexandrian, A. Cerracchio, C. Gregg, S. Haile, R. Kyskan, S. Milijevic, D. Oren, J. Solomon, et al. 2005. Dynamic ergosterol- and ceramide-rich domains in the peroxisomal membrane serve as an organizing platform for peroxisome fusion. J. Cell Biol. 168:761–773. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

