Orphan glutamate receptor delta1 subunit required for high-frequency hearing
- PMID: 17438141
- PMCID: PMC1900048
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02051-06
Orphan glutamate receptor delta1 subunit required for high-frequency hearing
Abstract
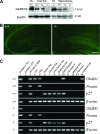
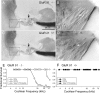
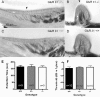
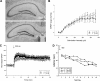
The function of the orphan glutamate receptor delta subunits (GluRdelta1 and GluRdelta2) remains unclear. GluRdelta2 is expressed exclusively in the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum, and GluRdelta1 is prominently expressed in inner ear hair cells and neurons of the hippocampus. We found that mice lacking the GluRdelta1 protein displayed significant cochlear threshold shifts for frequencies of >16 kHz. These deficits correlated with a substantial loss of type IV spiral ligament fibrocytes and a significant reduction of endolymphatic potential in high-frequency cochlear regions. Vulnerability to acoustic injury was significantly enhanced; however, the efferent innervation of hair cells and the classic efferent inhibition of outer hair cells were unaffected. Hippocampal and vestibular morphology and function were normal. Our findings show that the orphan GluRdelta1 plays an essential role in high-frequency hearing and ionic homeostasis in the basal cochlea, and the locus encoding GluRdelta1 represents a candidate gene for congenital or acquired high-frequency hearing loss in humans.
Figures

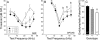

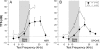

References
-
- Antoli-Candela, F. J., and N. Y. S. Kiang. 1978. Unit activity underlying the N1 potential, p. 165-191. In R. F. Naunton and C. Fernández (ed.), Evoked electrical activity in the auditory nervous system. Academic Press, New York, NY.
-
- Ben-Yosef, T., I. A. Belyantseva, T. L. Saunders, E. D. Hughes, K. Kawamoto, C. M. Van Itallie, L. A. Beyer, K. Halsey, D. J. Gardner, E. R. Wilcox, J. Rasmussen, J. M. Anderson, D. F. Dolan, A. Forge, Y. Raphael, S. A. Camper, and T. B. Friedman. 2003. Claudin 14 knockout mice, a model for autosomal recessive deafness DFNB29, are deaf due to cochlear hair cell degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12:2049-2061. - PubMed
-
- Boettger, T., C. A. Hubner, H. Maier, M. B. Rust, F. X. Beck, and T. J. Jentsch. 2002. Deafness and renal tubular acidosis in mice lacking the K-Cl co-transporter Kcc4. Nature 416:874-878. - PubMed
-
- Cohen-Salmon, M., T. Ott, V. Michel, J. P. Hardelin, I. Perfettini, M. Eybalin, T. Wu, D. C. Marcus, P. Wangemann, K. Willecke, and C. Petit. 2002. Targeted ablation of connexin26 in the inner ear epithelial gap junction network causes hearing impairment and cell death. Curr. Biol. 12:1106-1111. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DC006443/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC05168/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC06471/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC04477/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- CA21765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DC0188/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DC005209/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC05761/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DC005168/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DC005761/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DC000188/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC006471/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC000188/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DC05209/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DC005761/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC04761/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
