The role of Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 17440180
- PMCID: PMC1942130
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.111872
The role of Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
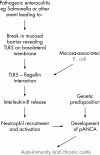
Mucosa‐associated E Coli are reported to be increased in Crohn's disease
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JMR is a past/present member of advisory boards for Procter and Gamble, Schering‐Plough, Chiesi, Falk, and Celltech/UCB, and, with the University of Liverpool and Provexis UK, holds a patent for use of a soluble fibre preparation as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease.
Comment on
-
High prevalence of Escherichia coli belonging to the B2+D phylogenetic group in inflammatory bowel disease.Gut. 2007 May;56(5):669-75. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.099796. Epub 2006 Oct 6. Gut. 2007. PMID: 17028128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Subramanian S, Campbell B J, Rhodes J M. Bacteria in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Infect Dis 200619475–484. - PubMed
-
- Egert M, de Graaf A A, Smidt H.et al Beyond diversity: functional microbiomics of the human colon. Trends Microbiol 20061486–91. - PubMed
-
- Atuma C, Strugala V, Allen A.et al The adherent gastrointestinal mucus gel layer: thickness and physical state in vivo. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2001280G922–G929. - PubMed
-
- Saldena T A, Saravi F D, Hwang H J.et al Oxygen diffusive barriers of rat distal colon: role of subepithelial tissue, mucosa, and mucus gel layer. Dig Dis Sci 2000452108–2114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical