Soluble epoxide hydrolase: a novel therapeutic target in stroke
- PMID: 17440491
- PMCID: PMC2664093
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600494
Soluble epoxide hydrolase: a novel therapeutic target in stroke
Abstract
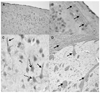
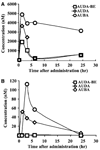
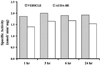
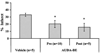
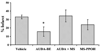
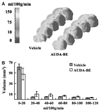
The P450 eicosanoids epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) are produced in brain and perform important biological functions, including protection from ischemic injury. The beneficial effect of EETs, however, is limited by their metabolism via soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). We tested the hypothesis that sEH inhibition is protective against ischemic brain damage in vivo by a mechanism linked to enhanced cerebral blood flow (CBF). We determined expression and distribution of sEH immunoreactivity (IR) in brain, and examined the effect of sEH inhibitor 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid butyl ester (AUDA-BE) on CBF and infarct size after experimental stroke in mice. Mice were administered a single intraperitoneal injection of AUDA-BE (10 mg/kg) or vehicle at 30 mins before 2-h middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) or at reperfusion, in the presence and absence of P450 epoxygenase inhibitor N-methylsulfonyl-6-(2-propargyloxyphenyl) hexanamide (MS-PPOH). Immunoreactivity for sEH was detected in vascular and non-vascular brain compartments, with predominant expression in neuronal cell bodies and processes. 12-(3-Adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid butyl ester was detected in plasma and brain for up to 24 h after intraperitoneal injection, which was associated with inhibition of sEH activity in brain tissue. Finally, AUDA-BE significantly reduced infarct size at 24 h after MCAO, which was prevented by MS-PPOH. However, regional CBF rates measured by iodoantipyrine (IAP) autoradiography at end ischemia revealed no differences between AUDA-BE- and vehicle-treated mice. The findings suggest that sEH inhibition is protective against ischemic injury by non-vascular mechanisms, and that sEH may serve as a therapeutic target in stroke.
Figures

References
-
- Alkayed NJ, Birks EK, Hudetz AG, Roman RJ, Henderson L, Harder DR. Inhibition of brain P-450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase decreases baseline cerebral blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1996a;271:H1541–H1546. - PubMed
-
- Alkayed NJ, Birks EK, Narayanan J, Petrie KA, Kohler-Cabot AE, Harder DR. Role of P-450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase in the response of cerebral blood flow to glutamate in rats. Stroke. 1997;28:1066–1072. - PubMed
-
- Alkayed NJ, Goyagi T, Joh HD, Klaus J, Harder DR, Traystman RJ, Hurn PD. Neuroprotection and P4502C11 upregulation after experimental transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2002;33:1677–1684. - PubMed
-
- Alkayed NJ, Narayanan J, Gebremedhin D, Medhora M, Roman RJ, Harder DR. Molecular characterization of an arachidonic acid epoxygenase in rat brain astrocytes. Stroke. 1996b;27:971–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ES02710/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS049210/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS049210/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS44313/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ES004699/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES002710/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM031278/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL59699-06A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 ES002710/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059699/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044313/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM31278/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES004699/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

