Epicutaneous immunization with type II collagen inhibits both onset and progression of chronic collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 17440622
- PMCID: PMC1849892
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000387
Epicutaneous immunization with type II collagen inhibits both onset and progression of chronic collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
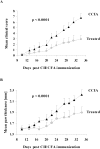
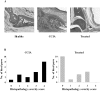
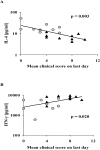
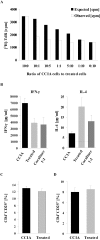
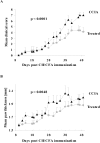
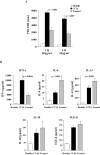
Epicutaneous immunization is a potential non-invasive technique for antigen-specific immune-modulation. Topical application of protein antigens to barrier-disrupted skin induces potent antigen-specific immunity with a strong Th2-bias. In this study, we investigate whether the autoimmune inflammatory response of chronic collagen-induced arthritis (CCIA) in DBA/1-TCR-beta Tg mice can be modified by epicutaneous immunization. We show that epicutaneous immunization with type II collagen (CII) inhibited development and progression of CCIA and, importantly, also ameliorated ongoing disease as indicated by clinical scores of disease severity, paw swelling and joints histology. Treated mice show reduced CII-driven T cell proliferation and IFN-gamma production, as well as significantly lower levels of CII-specific IgG2a serum antibodies. In contrast, CII-driven IL-4 production and IgE antibody levels were increased consistent with skewing of the CII response from Th1 to Th2 in treated mice. IL-4 production in treated mice was inversely correlated with disease severity. Moreover, T cells from treated mice inhibited proliferation and IFN-gamma production by T cells from CCIA mice, suggesting induction of regulatory T cells that actively inhibit effector responses in arthritic mice. The levels of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells were however not increased following epicutaneous CII treatment. Together, these results suggest that epicutaneous immunization may be used as an immune-modulating procedure to actively re-programme pathogenic Th1 responses, and could have potential as a novel specific and simple treatment for chronic autoimmune inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

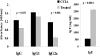
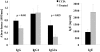
Similar articles
-
Oral administration of type-II collagen peptide 250-270 suppresses specific cellular and humoral immune response in collagen-induced arthritis.Clin Immunol. 2007 Jan;122(1):75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.08.004. Epub 2006 Oct 11. Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17045846
-
Down-regulation of Th1-mediated pathology in experimental arthritis by stimulation of the Th2 arm of the immune response.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Mar;48(3):839-45. doi: 10.1002/art.10832. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12632440
-
Induction of IL-10-producing CD4+CD25+ T cells in animal model of collagen-induced arthritis by oral administration of type II collagen.Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(3):R213-9. doi: 10.1186/ar1169. Epub 2004 Mar 11. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004. PMID: 15142267 Free PMC article.
-
Type II collagen autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis.Am J Med Sci. 2004 Apr;327(4):202-11. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200404000-00006. Am J Med Sci. 2004. PMID: 15084916 Review.
-
Skin-induced tolerance as a new needle free therapeutic strategy.Pharmacol Rep. 2014 Apr;66(2):192-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2013.09.001. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Pharmacol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24911069 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel BLyS Peptibody Down-Regulates B Cell and T Helper Cell Subsets In Vivo and Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis.Inflammation. 2016 Apr;39(2):839-48. doi: 10.1007/s10753-016-0314-6. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26861221
-
Gait analysis in a murine model of collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(6):R123. doi: 10.1186/ar2331. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 18036238 Free PMC article.
-
Glycyrol suppresses collagen-induced arthritis by regulating autoimmune and inflammatory responses.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 18;9(7):e98137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098137. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25036817 Free PMC article.
-
Epicutaneous immunization with TNP-Ig and Zymosan induces TCRαβ+ CD4+ contrasuppressor cells that reverse skin-induced suppression via IL-17A.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014;164(2):122-36. doi: 10.1159/000363446. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24993442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strid J, Hourihane J, Kimber I, Callard R, Strobel S. Disruption of the stratum corneum allows potent epicutaneous immunization with protein antigens resulting in a dominant systemic Th2 response. Eur J Immunol. 2204;34:2100–2109. - PubMed
-
- Wang LF, Lin JY, Hsieh KH, Lin RH. Epicutaneous exposure of protein antigen induces a predominant Th2-like response with high IgE production in mice. J Immunol. 1996;156:4077–4082. - PubMed
-
- Herrick CA, Xu L, McKenzie AN, Tigelaar RE, Bottomly K. IL-13 is necessary, not simply sufficient, for epicutaneously induced Th2 responses to soluble protein antigen. J Immunol. 2003;170:2488–2495. - PubMed
-
- Glenn GM, Taylor DN, Li X, Frankel S, Montemarano A, et al. Transcutaneous immunization: a human vaccine delivery strategy using a patch. Nat Med. 2000;6:1403–1406. - PubMed
-
- Partidos CD, Beignon AS, Briand JP, Muller S. Modulation of immune responses with transcutaneously deliverable adjuvants. Vaccine. 2004;22:2385–2390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

