Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease cleaves procaspase 8 in vivo
- PMID: 17442709
- PMCID: PMC1933285
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02798-06
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease cleaves procaspase 8 in vivo
Abstract
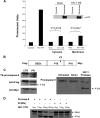
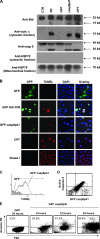
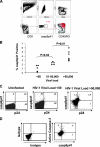
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection causes apoptosis of infected CD4 T cells as well as uninfected (bystander) CD4 and CD8 T cells. It remains unknown what signals cause infected cells to die. We demonstrate that HIV-1 protease specifically cleaves procaspase 8 to create a novel fragment termed casp8p41, which independently induces apoptosis. casp8p41 is specific to HIV-1 protease-induced death but not other caspase 8-dependent death stimuli. In HIV-1-infected patients, casp8p41 is detected only in CD4(+) T cells, predominantly in the CD27(+) memory subset, its presence increases with increasing viral load, and it colocalizes with both infected and apoptotic cells. These data indicate that casp8p41 independently induces apoptosis and is a specific product of HIV-1 protease which may contribute to death of HIV-1-infected cells.
Figures


References
-
- Adams, L. D., A. G. Tomasselli, P. Robbins, B. Moss, and R. L. Heinrikson. 1992. HIV-1 protease cleaves actin during acute infection of human T-lymphocytes. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 8:291-295. - PubMed
-
- Blanco, R., L. Carrasco, and I. Ventoso. 2003. Cell killing by HIV-1 protease. J. Biol. Chem. 278:1086-1093. - PubMed
-
- Boatright, K. M., M. Renatus, F. L. Scott, S. Sperandio, H. Shin, I. M. Pedersen, J. E. Ricci, W. A. Edris, D. P. Sutherlin, D. R. Green, and G. S. Salvesen. 2003. A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol. Cell 11:529-541. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley, J. M., B. J. Hill, D. R. Ambrozak, D. A. Price, F. J. Guenaga, J. P. Casazza, J. Kuruppu, J. Yazdani, S. A. Migueles, M. Connors, M. Roederer, D. C. Douek, and R. A. Koup. 2004. T-cell subsets that harbor human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in vivo: implications for HIV pathogenesis. J. Virol. 78:1160-1168. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

