Changes in Sef levels influence auditory brainstem development and function
- PMID: 17442811
- PMCID: PMC6672320
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3477-06.2007
Changes in Sef levels influence auditory brainstem development and function
Abstract
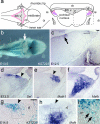
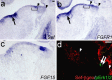
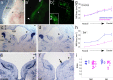
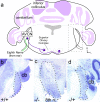
During development of the CNS, secreted morphogens of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family have multiple effects on cell division, migration, and survival depending on where, when, and how much FGF signal is received. The consequences of misregulating the FGF pathway were studied in a mouse with decreased levels of the FGF antagonist Sef. To uncover effects in the nervous system, we focused on the auditory system, which is accessible to physiological analysis. We found that the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is active in the rhombic lip, a germinal zone that generates diverse types of neurons, including the cochlear nucleus complex of the auditory system. Sef is expressed immediately adjacent to the rhombic lip, overlapping with FGF15 and FGFR1, which is also present in the lip itself. This pattern suggests that Sef may normally function in non-rhombic lip cells and prevent them from responding to FGF ligand in the vicinity. Consistent with this idea, overexpression of Sef in chicks decreased the size of the auditory nuclei. Cochlear nucleus defects were also apparent in mice with reduced levels of Sef, with 13% exhibiting grossly dysmorphic cochlear nuclei and 26% showing decreased amounts of GFAP in the cochlear nucleus. Additional evidence for cochlear nucleus defects was obtained by electrophysiological analysis of Sef mutant mice, which have normal auditory thresholds but abnormal auditory brainstem responses. These results show both increases and decreases in Sef levels affect the assembly and function of the auditory brainstem.
Figures

References
-
- Basson MA, Akbulut S, Watson-Johnson J, Simon R, Carroll TJ, Shakya R, Gross I, Martin GR, Lufkin T, McMahon AP, Wilson PD, Costantini FD, Mason IJ, Licht JD. Sprouty1 is a critical regulator of GDNF/RET-mediated kidney induction. Dev Cell. 2005;8:229–239. - PubMed
-
- Cramer KS, Fraser SE, Rubel EW. Embryonic origins of auditory brainstem nuclei in the chick hindbrain. Dev Biol. 2000;224:138–151. - PubMed
-
- Cramer KS, Bermingham-McDonogh O, Krull CE, Rubel EW. EphA4 signaling promotes axon segregation in the developing auditory system. Dev Biol. 2004;269:26–35. - PubMed
-
- Cramer KS, Cerretti DP, Siddiqui SA. EphB2 regulates axonal growth at the midline in the developing auditory brainstem. Dev Biol. 2006;295:76–89. - PubMed
-
- Darby S, Sahadevan K, Khan MM, Robson CN, Leung HY, Gnanapragasam VJ. Loss of Sef (similar expression to FGF) expression is associated with high grade and metastatic prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25:4122–4127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
