Statistical significance of quantitative PCR
- PMID: 17445280
- PMCID: PMC1868764
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-131
Statistical significance of quantitative PCR
Abstract
Background: PCR has the potential to detect and precisely quantify specific DNA sequences, but it is not yet often used as a fully quantitative method. A number of data collection and processing strategies have been described for the implementation of quantitative PCR. However, they can be experimentally cumbersome, their relative performances have not been evaluated systematically, and they often remain poorly validated statistically and/or experimentally. In this study, we evaluated the performance of known methods, and compared them with newly developed data processing strategies in terms of resolution, precision and robustness.
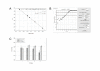
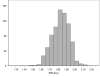
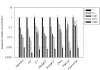
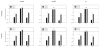
Results: Our results indicate that simple methods that do not rely on the estimation of the efficiency of the PCR amplification may provide reproducible and sensitive data, but that they do not quantify DNA with precision. Other evaluated methods based on sigmoidal or exponential curve fitting were generally of both poor resolution and precision. A statistical analysis of the parameters that influence efficiency indicated that it depends mostly on the selected amplicon and to a lesser extent on the particular biological sample analyzed. Thus, we devised various strategies based on individual or averaged efficiency values, which were used to assess the regulated expression of several genes in response to a growth factor.
Conclusion: Overall, qPCR data analysis methods differ significantly in their performance, and this analysis identifies methods that provide DNA quantification estimates of high precision, robustness and reliability. These methods allow reliable estimations of relative expression ratio of two-fold or higher, and our analysis provides an estimation of the number of biological samples that have to be analyzed to achieve a given precision.
Figures

References
-
- Ailenberg M, Silverman M. Controlled hot start and improved specificity in carrying out PCR utilizing touch-up and loop incorporated primers (TULIPS) Biotechniques. 2000;29:1018–20, 1022-4. - PubMed
-
- Etienne W, Meyer MH, Peppers J, Meyer RA., Jr. Comparison of mRNA gene expression by RT-PCR and DNA microarray. Biotechniques. 2004;36:618–20, 622, 624-6. - PubMed
-
- Wittwer CT, Herrmann MG, Moss AA, Rasmussen RP. Continuous fluorescence monitoring of rapid cycle DNA amplification. Biotechniques. 1997;22:130–1, 134-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

