Translation of nonSTOP mRNA is repressed post-initiation in mammalian cells
- PMID: 17446866
- PMCID: PMC1864977
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601679
Translation of nonSTOP mRNA is repressed post-initiation in mammalian cells
Abstract
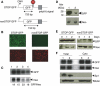
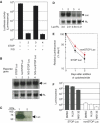
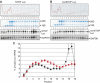
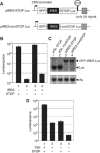
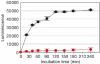
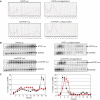
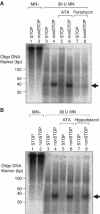
We investigated the fate of aberrant mRNAs lacking in-frame termination codons (called nonSTOP mRNA) in mammalian cells. We found that translation of nonSTOP mRNA was considerably repressed although a corresponding reduction of mRNA was not observed. The repression appears to be post-initiation since (i) repressed nonSTOP mRNAs were associated with polysomes, (ii) translation of IRES-initiated and uncapped nonSTOP mRNA were repressed, and (iii) protein production from nonSTOP mRNA associating with polysomes was significantly reduced when used to program an in vitro run-off translation assay. NonSTOP mRNAs distributed into lighter polysome fractions compared to control mRNAs encoding a stop codon, and a significant amount of heterogeneous polypeptides were produced during in vitro translation of nonSTOP RNAs, suggesting premature termination of ribosomes translating nonSTOP mRNA. Moreover, a run-off translation assay using hippuristanol and RNAse protection assays suggested the presence of a ribosome stalled at the 3' end of nonSTOP mRNAs. Taken together, these data indicate that ribosome stalling at the 3' end of nonSTOP mRNAs can block translation by preventing upstream translation events.
Figures

References
-
- Amrani N, Sachs MS, Jacobson A (2006) Early nonsense: mRNA decay solves a translational problem. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 415–425 - PubMed
-
- Baker KE, Parker R (2004) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: terminating erroneous gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16: 293–299 - PubMed
-
- Behm-Ansmant I, Izaurralde E (2006) Quality control of gene expression: a stepwise assembly pathway for the surveillance complex that triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev 20: 391–398 - PubMed
-
- Bordeleau ME, Mori A, Oberer M, Lindqvist L, Chard LS, Higa T, Belsham GJ, Wagner G, Tanaka J, Pelletier J (2006) Functional characterization of IRESes by an inhibitor of the RNA helicase eIF4A. Nat Chem Biol 2: 213–220 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

