The synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO, suppresses alloreactive T cell responses and reduces murine early acute graft-versus-host disease mortality
- PMID: 17448911
- PMCID: PMC4559277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.12.453
The synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO, suppresses alloreactive T cell responses and reduces murine early acute graft-versus-host disease mortality
Abstract
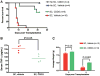
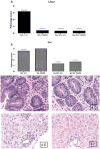
Acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) still remains one of the life-threatening complications following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Immunomodulation of alloreactive donor T cell responses, as well as cytokine secretion is a potential therapeutic approach for the prevention of aGVHD. The synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO (2-cyano-3, 12-dioxooleana-1, 9-dien-28-oic acid), exhibits potent antitumor activity and has also been shown to mediate anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. We therefore wanted to assess the effects of CDDO on early lethal aGVHD. In this study, we found that CDDO significantly inhibited in vitro mixed lymphocyte responses and preferentially promoted the apoptosis of proliferating but not resting alloreactive T cells. Using a full major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-disparate murine aGVHD model, we found that the administration of CDDO immediately after transplantation significantly decreased liver pathology as determined by histologic assessment and prolonged survival in mice. Importantly, administration of CDDO did not adversely impair donor myeloid reconstitution as determined by peripheral blood cell count and the extent of donor chimerism. These findings indicate that CDDO has a significant immunomodulatory effects in vitro and on early lethal aGVHD development, particularly affecting the liver, in a murine allo-HSCT model.
Figures



References
-
- Fowler DH. Shared biology of GVHD and GVT effects: potential methods of separation. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006;57:225–244. - PubMed
-
- Murphy GF, Korngold R. Significance of selectively targeted apoptotic rete cells in graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2004;10:357–365. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara JL, Reddy P. Pathophysiology of graft-versus-host disease. Semin Hematol. 2006;43:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Ray DM, Morse KM, Hilchey SP, et al. The novel triterpenoid 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO) induces apoptosis of human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells through a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-independent pathway. Exp Hematol. 2006;34:1201–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

