Highly ordered nanowire arrays on plastic substrates for ultrasensitive flexible chemical sensors
- PMID: 17450146
- PMCID: PMC3695594
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat1891
Highly ordered nanowire arrays on plastic substrates for ultrasensitive flexible chemical sensors
Abstract
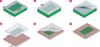
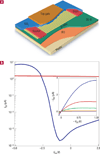
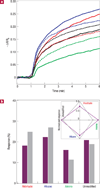
The development of a robust method for integrating high-performance semiconductors on flexible plastics could enable exciting avenues in fundamental research and novel applications. One area of vital relevance is chemical and biological sensing, which if implemented on biocompatible substrates, could yield breakthroughs in implantable or wearable monitoring systems. Semiconducting nanowires (and nanotubes) are particularly sensitive chemical sensors because of their high surface-to-volume ratios. Here, we present a scalable and parallel process for transferring hundreds of pre-aligned silicon nanowires onto plastic to yield highly ordered films for low-power sensor chips. The nanowires are excellent field-effect transistors, and, as sensors, exhibit parts-per-billion sensitivity to NO2, a hazardous pollutant. We also use SiO2 surface chemistries to construct a 'nano-electronic nose' library, which can distinguish acetone and hexane vapours via distributed responses. The excellent sensing performance coupled with bendable plastic could open up opportunities in portable, wearable or even implantable sensors.
Figures


References
-
- Service RF. Inorganic electronics begin to flex their muscle. Science. 2006;312:1593–1594. - PubMed
-
- Reuss RH, et al. Macroelectronics: Perspectives on technology and applications. Proc. IEEE. 2005;93:1239–1256.
-
- Xu JM. Plastic electronics and future trends in microelectronics. Synth. Met. 2000;115:1–3.
-
- Uchikoga S. Low-temperature polycrystalline silicon thin-film transistor technologies for system-on-glass displays. Mater. Res. Soc. Bull. 2002;27:881–885.
-
- Gosain DP, Noguchi T, Usui S. High mobility thin film transistors fabricated on a plastic substrate at a processing temperature of 110 °C. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000;39:L179–L181. 2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

