Adrenaline increases glucose transport via a Rap1-p38MAPK pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 17450172
- PMCID: PMC2013965
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707247
Adrenaline increases glucose transport via a Rap1-p38MAPK pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Adrenaline has been implicated in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. However, little is known regarding the role of adrenaline in glucose transport in VSMC.
Experimental approach: In this study, we examined the effects of adrenaline on glucose uptake in rat VSMC. We also examined the downstream signaling pathway from the beta-adrenoceptor to glucose uptake, using a pharmacological approach. To investigate the downstream action of adenylate cyclase, we studied the effects of GGTI-298, an inhibitor of geranylgeranylation of GTPases, including Rap1. To confirm the involvement of Rap1, we silenced Rap1 by siRNA.
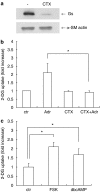
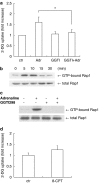
Key results: Adrenaline induced glucose uptake in a dose-dependent manner. The adrenaline-induced glucose uptake was inhibited by L-propranolol, (a selective beta-adrenoceptor antagonist), but not by prazosin (a selective alpha(1)-adrenoceptor antagonist) or UK14304 (a selective alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist), suggesting the involvement of beta-adrenoceptors in glucose transport. Long-term treatment with cholera toxin, which resulted in sequestration of G(s) proteins, prevented the adrenaline-induced glucose uptake. Forskolin, a direct activator of adenylate cyclase, was found to mimic the effects of adrenaline. Adrenaline-induced glucose uptake was inhibited by GGTI-298, not by H89 (a selective inhibitor of PKA). Silencing of Rap1 by siRNA attenuated the adrenaline-induced glucose uptake. Adrenaline-induced glucose uptake was inhibited by SB203580 (a selective inhibitor of p38MAPK) and adrenaline-induced p38MAPK activation was inhibited by GGTI-298 and siRNA against Rap1.
Conclusions and implications: These findings suggest that adrenaline-induced glucose transport is mediated by beta-adrenoceptors, G(s), adenylate cyclase, Rap1, and p38MAPK in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Figures





Comment in
-
More PKA independent beta-adrenergic signalling via cAMP: is Rap1-mediated glucose uptake in vascular smooth cells physiologically important?Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;151(4):423-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707248. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17450171 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
More PKA independent beta-adrenergic signalling via cAMP: is Rap1-mediated glucose uptake in vascular smooth cells physiologically important?Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;151(4):423-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707248. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17450171 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin-induced glucose transport via Src-p38 MAPK pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Sep;146(1):60-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706293. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15951827 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-I and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) regulate cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB)-dependent transcription via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in pituitary cells: requirement of Rap1.J Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jun;34(3):699-712. doi: 10.1677/jme.1.01703. J Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15956341
-
Responses of vascular smooth muscle cells to estrogen are dependent on balance between ERK and p38 MAPK pathway activities.Int J Cardiol. 2009 May 29;134(3):356-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.02.017. Epub 2008 Jun 26. Int J Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 18584900
-
PDTC, metal chelating compound, induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest in vascular smooth muscle cells through inducing p21Cip1 expression: involvement of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase.J Cell Physiol. 2004 Feb;198(2):310-23. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10728. J Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14603533
Cited by
-
Thrombospondin-1 stimulates platelet aggregation by blocking the antithrombotic activity of nitric oxide/cGMP signaling.Blood. 2008 Jan 15;111(2):613-23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-06-098392. Epub 2007 Sep 21. Blood. 2008. PMID: 17890448 Free PMC article.
-
NAD-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase as a novel target of tributyltin in human embryonic carcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2014 Aug 5;4:5952. doi: 10.1038/srep05952. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25092173 Free PMC article.
-
Rap1a is a key regulator of fibroblast growth factor 2-induced angiogenesis and together with Rap1b controls human endothelial cell functions.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(18):5803-10. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00393-08. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18625726 Free PMC article.
-
β2-adrenoceptor agonists can both stimulate and inhibit glucose uptake in mouse soleus muscle through ligand-directed signalling.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;386(9):761-73. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0860-5. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23564017
-
α-Melanocyte stimulating hormone promotes muscle glucose uptake via melanocortin 5 receptors.Mol Metab. 2016 Aug 5;5(10):807-822. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.07.009. eCollection 2016 Oct. Mol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27688995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bos JL. Epac: a new cAMP target and new avenues in cAMP research. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Chernogubova E, Cannon B, Bengtsson T. Norepinephrine increases glucose transport in brown adipocytes via β3-adrenoceptors through a cAMP, PKA and PI3-kinase-dependent pathway stimulating conventional and novel PKCs. Endocrinology. 2004;145:269–280. - PubMed
-
- de Rooij J, Zwartkruis FJ, Verheijen MH, Cool RH, Nijman SM, Wittinghofer A, et al. Epac is a Rap1 guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor directly activated by cyclic AMP. Nature. 1998;396:474–477. - PubMed
-
- Dimsdale JE, Moss J. Plasma catecholamines in stress and exercise. JAMA. 1980;243:340–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

