(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits growth of gastric cancer by reducing VEGF production and angiogenesis
- PMID: 17451194
- PMCID: PMC4146988
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1162
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits growth of gastric cancer by reducing VEGF production and angiogenesis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on growth of gastric cancer and its possible mechanism.
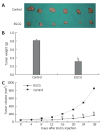
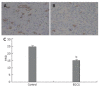
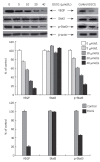
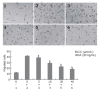
Methods: Heterotopic tumors were induced by subcutaneously injection of SGC-7901 cells in nude mice. Tumor growth was measured by calipers in two dimensions. Tumor angiogenesis was determined with tumor microvessel density (MVD) by immunohistology. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein level and activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) were examined by Western blotting. VEGF mRNA expression was determined by RT-PCR and VEGF release in tumor culture medium by ELISA. VEGF-induced cell proliferation was studied by MTT assay, cell migration by gelatin modified Boyden chamber (Transwell) and in vitro angiogenesis by endothelial tube formation in Matrigel.
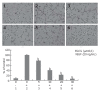
Results: Intraperitoneal injection of EGCG inhibited the growth of gastric cancer by 60.4%. MVD in tumor tissues treated with EGCG was markedly reduced. EGCG treatment reduced VEGF protein level in vitro and in vivo. Secretion and mRNA expression of VEGF in tumor cells were also suppressed by EGCG in a dose-dependent manner. This inhibitory effect was associated with reduced activation of Stat3, but EGCG treatment did not change the total Stat3 expression. EGCG also inhibited VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration and tube formation.
Conclusion: EGCG inhibits the growth of gastric cancer by reducing VEGF production and angiogenesis, and is a promising candidate for anti-angiogenic treatment of gastric cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits growth and angiogenesis of gastric cancer and its molecular mechanism].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Jan;12(1):82-5. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19145512 Chinese.
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits VEGF expression induced by IL-6 via Stat3 in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 May 14;17(18):2315-25. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i18.2315. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21633597 Free PMC article.
-
[(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric cancer cells via suppressing activity].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Aug;14(8):631-5. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21866460 Chinese.
-
The Epigenetic Modification of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) on Cancer.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(11):1099-1104. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666200504080112. Curr Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32364072 Review.
-
The Role of EGCG in Breast Cancer Prevention and Therapy.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(7):883-898. doi: 10.2174/1389557520999201211194445. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33319659 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Therapeutic Targets of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG), the Most Abundant Catechin in Green Tea, and Its Role in the Therapy of Various Types of Cancer.Molecules. 2020 Jul 9;25(14):3146. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143146. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32660101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathways in cancer angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by natural compounds: a comprehensive and critical review.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Mar;43(1):501-574. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10136-9. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 37792223 Review.
-
Real Time Monitoring of Inhibition of Adipogenesis and Angiogenesis by (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.Nutrients. 2015 Oct 27;7(10):8871-86. doi: 10.3390/nu7105437. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 26516907 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Strategies of Gastric Cancer-Molecular Targets for Anti-angiogenic Therapy: a State-of-the-art Review.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021 Jun;52(2):476-488. doi: 10.1007/s12029-021-00629-7. Epub 2021 Mar 24. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33761051 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of soy and tea in prostate cancer prevention.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2010 Jun;235(6):659-67. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2010.009335. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2010. PMID: 20511670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide incidence of eighteen major cancers in 1985. Int J Cancer. 1993;54:594–606. - PubMed
-
- Kelley JR, Duggan JM. Gastric cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Daniel KG, Kuhn DJ, Kazi A, Bhuiyan M, Li L, Wang Z, Wan SB, Lam WH, Chan TH, et al. Green tea and tea polyphenols in cancer prevention. Front Biosci. 2004;9:2618–2631. - PubMed
-
- Yamane T, Takahashi T, Kuwata K, Oya K, Inagake M, Kitao Y, Suganuma M, Fujiki H. Inhibition of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced carcinogenesis by (-)-epigallocatechin gallate in the rat glandular stomach. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2081–2084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

