Antisense oligonucleotide targeting midkine suppresses in vivo angiogenesis
- PMID: 17451201
- PMCID: PMC4146995
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1208
Antisense oligonucleotide targeting midkine suppresses in vivo angiogenesis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effect of antisense oligonucleotide targeting midkine (MK-AS) on angiogenesis in chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) and in situ human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
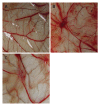
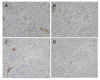
Methods: An in situ human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model and CAM assay were used in this experiment. The effect of MK-AS on angiogenesis was evaluated by cell proliferation assay and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining.
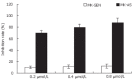
Results: MK-AS significantly inhibited human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and in situ human HCC growth. At the same time, MK-AS suppressed the angiogenesis both in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HEPG2)-induced CAM and in situ human HCC tissues.
Conclusion: MK-AS is an effective antiangiogenesis agent in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Folkman J, Tumor angiogenesis. In: Mendelsohn J, Howley P, Liotta LA, and Israel M, editors. The Molecular Basis of Cancer. Philadelphia: Saunders WB; 1995. p. 206–232.
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Campbell SC, Volpert OV, Ivanovich M, Bouck NP. Molecular mediators of angiogenesis in bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58:1298–1304. - PubMed
-
- Distler JH, Hirth A, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Gay RE, Gay S, Distler O. Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med. 2003;47:149–161. - PubMed
-
- O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J. Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell. 1997;88:277–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

