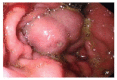
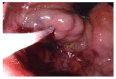
Prevalence of gastric varices and results of sclerotherapy with N-butyl 2 cyanoacrylate for controlling acute gastric variceal bleeding
- PMID: 17451208
- PMCID: PMC4147002
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1247
Prevalence of gastric varices and results of sclerotherapy with N-butyl 2 cyanoacrylate for controlling acute gastric variceal bleeding
Abstract
Aim: To study the prevalence, predictors and control of bleeding following N-butyl 2 cyanoacrylate (NBC) sclerotherapy of gastric varix (GV).
Methods: We analyzed case records of 1436 patients with portal hypertension, who underwent endoscopy during the past five years for variceal screening or upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. Fifty patients with bleeding GV underwent sclerotherapy with a mean of 2 mL NBC for control of bleeding. Outcome parameters were primary hemostasis (bleeding control within the first 48 h), recurrent bleeding (after 48 h of esophago-gastro-duodenoscopy) and in-hospital mortality were analyzed.
Results: The prevalence of GV in patients with portal hypertension was 15% (220/1436) and the incidence of bleeding was 22.7% (50/220). Out of the 50 bleeding GV patients, isolated gastric varices (IGV-I) were seen in 22 (44%), gastro-oesophageal varices (GOV) on lesser curvature (GOV-I) in 16 (32%), and GOV on greater curvature (GOV-II) in 15 (30%). IGV-I was seen in 44% (22/50) patients who had bleeding as compared to 23% (39/170) who did not have bleeding (P < 0.003). Primary hemostasis was achieved with NBC in all patients. Re-bleeding occurred in 7 (14%) patients after 48 h of initial sclerotherapy. Secondary hemostasis was achieved with repeat NBC sclerotherapy in 4/7 (57%). Three patients died after repeat sclerotherapy, one during transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stem shunt (TIPSS), one during surgery and one due to uncontrolled bleeding. Treatment failure-related mortality rate was 6% (3/50).
Conclusion: GV can be seen in 15% of patients with portal hypertension and the incidence of bleeding is 22.7%. NBC is highly effective in controlling GV bleeding. In hospital mortality of patients with bleeding GV is 6%.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoscopic hemostasis for bleeding gastric varices treated by combination of variceal ligation and sclerotherapy with N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate.J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jul;42(7):528-32. doi: 10.1007/s00535-007-2041-0. Epub 2007 Jul 25. J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17653647 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of undiluted N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in the endoscopic treatment of upper gastrointestinal tract varices.Endoscopy. 1996 Feb;28(2):239-43. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005435. Endoscopy. 1996. PMID: 8739740
-
Band ligation vs. N-Butyl-2-cyanoacrylate injection in acute gastric variceal bleeding: a prospective follow-up study.Ann Hepatol. 2013 Jan-2014 Feb;13(1):75-83. Ann Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 24378269 Clinical Trial.
-
Cyanoacrylate glue in the management of gastric varices.Minerva Med. 2009 Feb;100(1):115-21. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Minerva Med. 2009. PMID: 19078888 Review.
-
Management of acute gastric varices bleeding.J Chin Med Assoc. 2013 Oct;76(10):539-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jul 20. J Chin Med Assoc. 2013. PMID: 23880574 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of N-Butyl 2 Cyanoacrylate Injection for Treatment of Gastric Varices: A five year experience from a tertiary care hospital in Karachi, Pakistan.Pak J Med Sci. 2022 May-Jun;38(5):1360-1365. doi: 10.12669/pjms.38.5.4999. Pak J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35799731 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic management of gastric variceal bleeding with cyanoacrylate glue injection: safety and efficacy in a Canadian population.Can J Gastroenterol. 2010 Oct;24(10):593-6. doi: 10.1155/2010/276273. Can J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21037987 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes of gastric variceal obliteration using N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in patients with acute gastric variceal hemorrhage.Korean J Intern Med. 2014 Jul;29(4):437-44. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2014.29.4.437. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Korean J Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 25045291 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of endoscopic N-Butyl-2 Cyanoacrylate injection for the treatment of bleeding gastric varices in children.Pak J Med Sci. 2018 Nov-Dec;34(6):1363-1368. doi: 10.12669/pjms.346.16044. Pak J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30559786 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Outcomes and Their Determinants in Patients With Gastric Variceal Bleed Undergoing Endoscopic Cyanoacrylate Injection: An Observational Study.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024 May-Jun;14(3):101315. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.101315. Epub 2023 Dec 21. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38283706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soehendra N, Grimm H, Nam VC, Berger B. N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate: a supplement to endoscopic sclerotherapy. Endoscopy. 1987;19:221–224. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K, Kimura K, Matsutani S, Ohto M, Okuda K. Portal hemodynamics in patients with gastric varices. A study in 230 patients with esophageal and/or gastric varices using portal vein catheterization. Gastroenterology. 1988;95:434–440. - PubMed
-
- Sarin SK, Kumar A. Gastric varices: profile, classification, and management. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989;84:1244–1249. - PubMed
-
- Lo GH, Lai KH, Cheng JS, Chen MH, Chiang HT. A prospective, randomized trial of butyl cyanoacrylate injection versus band ligation in the management of bleeding gastric varices. Hepatology. 2001;33:1060–1064. - PubMed
-
- Sarin SK, Lahoti D, Saxena SP, Murthy NS, Makwana UK. Prevalence, classification and natural history of gastric varices: a long-term follow-up study in 568 portal hypertension patients. Hepatology. 1992;16:1343–1349. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous