Human tribbles-1 controls proliferation and chemotaxis of smooth muscle cells via MAPK signaling pathways
- PMID: 17452330
- PMCID: PMC2366084
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M610792200
Human tribbles-1 controls proliferation and chemotaxis of smooth muscle cells via MAPK signaling pathways
Abstract
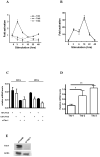
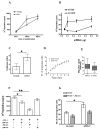
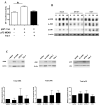
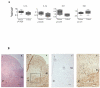
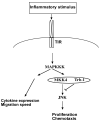
Migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells are key to a number of physiological and pathological processes, including wound healing and the narrowing of the vessel wall. Previous work has shown links between inflammatory stimuli and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation, although the molecular mechanisms of this process are poorly understood. Here we report that tribbles-1, a recently described modulator of MAPK activation, controls vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and chemotaxis via the Jun kinase pathway. Our findings demonstrate that this regulation takes place via direct interactions between tribbles-1 and MKK4/SEK1, a Jun activator kinase. The activity of this kinase is dependent on tribbles-1 levels, whereas the activation and the expression of MKK4/SEK1 are not. In addition, tribbles-1 expression is elevated in human atherosclerotic arteries when compared with non-atherosclerotic controls, suggesting that this protein may play a role in disease in vivo. In summary, the data presented here suggest an important regulatory role for trb-1 in vascular smooth muscle cell biology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modification of PI3K- and MAPK-dependent chemotaxis in aortic vascular smooth muscle cells by protein kinase CbetaII.Circ Res. 2005 Feb 4;96(2):197-206. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000152966.88353.9d. Epub 2004 Dec 9. Circ Res. 2005. PMID: 15591231
-
Glucose-potentiated chemotaxis in human vascular smooth muscle is dependent on cross-talk between the PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways.Circ Res. 2004 Aug 20;95(4):380-8. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000138019.82184.5d. Epub 2004 Jul 8. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15242975
-
Urokinase-induced smooth muscle cell responses require distinct signaling pathways: a role for the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Vasc Surg. 2005 Apr;41(4):672-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.01.007. J Vasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 15874933
-
Role of PI3K/AKT, cPLA2 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in insulin regulation of vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Sep;9(3):172-80. doi: 10.2174/187152909789007034. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19534657 Review.
-
Tribbles in inflammation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Oct;43(5):1069-74. doi: 10.1042/BST20150095. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 26517925 Review.
Cited by
-
TRIB2 regulates normal and stress-induced thymocyte proliferation.Cell Discov. 2016 Mar 15;2:15050. doi: 10.1038/celldisc.2015.50. eCollection 2016. Cell Discov. 2016. PMID: 27462446 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated inhibition of C/EBP by Tribbles in multiple tissues is essential for Caenorhabditis elegans development.BMC Biol. 2016 Dec 7;14(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0320-z. BMC Biol. 2016. PMID: 27927209 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced macrophage tribbles-1 expression in murine experimental atherosclerosis.Biology (Basel). 2012 Apr 10;1(1):43-57. doi: 10.3390/biology1010043. Biology (Basel). 2012. PMID: 24832046 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profile of rat genes in injured spinal cord at different stages by RNA-sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2017 Feb 15;18(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3532-x. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28201982 Free PMC article.
-
Aging deteriorated liver Ischemia and reperfusion injury by suppressing Tribble's proteins 1 mediated macrophage polarization.Bioengineered. 2022 Jun;13(6):14519-14533. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2090218. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 36694470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ju H, Nerurkar S, Sauermelch CF, Olzinski AR, Mirabile R, Zimmerman D, Lee JC, Adams J, Sisko J, Berova M, Willette RN. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;301:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Takeishi Y, Huang Q, Wang T, Glassman M, Yoshizumi M, Baines CP, Lee JD, Kawakatsu H, Che W, Lerner-Marmarosh N, Zhang C, Yan C, Ohta S, Walsh RA, Berk BC, Abe J. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33:1989–2005. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV, Force T. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1998;7:425–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

