Mature natural killer cell and lymphoid tissue-inducing cell development requires Id2-mediated suppression of E protein activity
- PMID: 17452521
- PMCID: PMC2118569
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20061959
Mature natural killer cell and lymphoid tissue-inducing cell development requires Id2-mediated suppression of E protein activity
Abstract
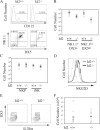
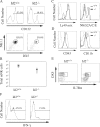
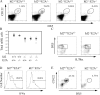
The Id2 transcriptional repressor is essential for development of natural killer (NK) cells, lymphoid tissue-inducing (LTi) cells, and secondary lymphoid tissues. Id2 was proposed to regulate NK and LTi lineage specification from multipotent progenitors through suppression of E proteins. We report that NK cell progenitors are not reduced in the bone marrow (BM) of Id2(-/-) mice, demonstrating that Id2 is not essential for NK lineage specification. Rather, Id2 is required for development of mature (m) NK cells. We define the mechanism by which Id2 functions by showing that a reduction in E protein activity, through deletion of E2A, overcomes the need for Id2 in development of BM mNK cells, LTi cells, and secondary lymphoid tissues. However, mNK cells are not restored in the blood or spleen of Id2(-/-)E2A(-/-) mice, suggesting a role for Id2 in suppression of alternative E proteins after maturation. Interestingly, the few splenic mNK cells in Id2(-/-) and Id2(-/-)E2A(-/-) mice have characteristics of thymus-derived NK cells, which develop in the absence of Id2, implying a differential requirement for Id2 in BM and thymic mNK development. Our findings redefine the essential functions of Id2 in lymphoid development and provide insight into the dynamic regulation of E and Id proteins during this process.
Figures


References
-
- Yokoyama, W.M., S. Kim, and A.R. French. 2004. They dynamic life of natural killer cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:405–429. - PubMed
-
- Vidal, S.M., and L.L. Lanier. 2006. NK cell recognition of mouse cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 298:183–206. - PubMed
-
- Stewart, C.A., E. Vivier, and M. Colonna. 2006. Strategies of natural killer cell recognition and signaling. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 298:1–21. - PubMed
-
- McNerney, M.E., and V. Kumar. 2006. The CD2 family of natural killer cell receptors. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 298:91–120. - PubMed
-
- Kondo, M., I.L. Weissman, and K. Akashi. 1997. Identification of clonogenic common lymphoid progenitors in mouse bone marrow. Cell. 91:661–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

