Pigeons combine compass and landmark guidance in familiar route navigation
- PMID: 17452634
- PMCID: PMC1863466
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0701575104
Pigeons combine compass and landmark guidance in familiar route navigation
Abstract
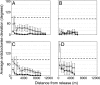
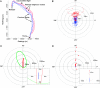
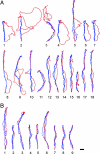
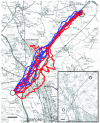
How do birds orient over familiar terrain? In the best studied avian species, the homing pigeon (Columba livia), two apparently independent primary mechanisms are currently debated: either memorized visual landmarks provide homeward guidance directly, or birds rely on a compass to home from familiar locations. Using miniature Global Positioning System tracking technology and clock-shift procedures, we set sun-compass and landmark information in conflict, showing that experienced birds can accurately complete their memorized routes by using landmarks alone. Nevertheless, we also find that route following is often consistently offset in the expected compass direction, faithfully reproducing the shape of the track, but in parallel. Thus, we demonstrate conditions under which compass orientation and landmark guidance must be combined into a system of simultaneous or oscillating dual control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Familiar route loyalty implies visual pilotage in the homing pigeon.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 14;101(50):17440-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406984101. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15572457 Free PMC article.
-
Homing pigeons develop local route stereotypy.Proc Biol Sci. 2005 Jan 7;272(1558):17-23. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2004.2873. Proc Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15875565 Free PMC article.
-
Homing in pigeons: the role of the hippocampal formation in the representation of landmarks used for navigation.J Neurosci. 1999 Jan 1;19(1):311-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-01-00311.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 9870960 Free PMC article.
-
Route following and the pigeon's familiar area map.J Exp Biol. 2014 Jan 15;217(Pt 2):169-79. doi: 10.1242/jeb.092908. J Exp Biol. 2014. PMID: 24431141 Review.
-
Cues indicating location in pigeon navigation.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2015 Oct;201(10):961-7. doi: 10.1007/s00359-015-1027-2. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26149606 Review.
Cited by
-
Customizable Recorder of Animal Kinesis (CRoAK): A multi-axis instrumented enclosure for measuring animal movements.HardwareX. 2020 Jun 10;8:e00116. doi: 10.1016/j.ohx.2020.e00116. eCollection 2020 Oct. HardwareX. 2020. PMID: 35498259 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal predictability drive foraging movements of coastal birds.Mov Ecol. 2025 Feb 1;13(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40462-025-00531-y. Mov Ecol. 2025. PMID: 39893488 Free PMC article.
-
Homing pigeons respond to time-compensated solar cues even in sight of the loft.PLoS One. 2013 May 24;8(5):e63130. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063130. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23717401 Free PMC article.
-
Learning to use landmarks for navigation amplifies their representation in retrosplenial cortex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 19:2024.08.18.607457. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.18.607457. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39229229 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Foraging on the wing for fish while migrating over changing landscapes: traveling behaviors vary with available aquatic habitat for Caspian terns.Mov Ecol. 2022 Mar 2;10(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40462-022-00307-8. Mov Ecol. 2022. PMID: 35236399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wallraff HG. Avian Navigation: Pigeon Homing as a Paradigm. Berlin: Springer; 2005.
-
- Papi F, editor. Animal Homing. London: Chapman & Hall; 1992.
-
- Baker RR. Bird Navigation: The Solution of a Mystery? London: Hodder & Staughton; 1984.
-
- Wallraff HG. Das Navigationssystem der Vögel. Munich: Oldenbourg; 1974.
-
- Wiltschko R, Wiltschko W. Anim Behav. 2003;65:257–272.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

