A monomeric G protein-coupled receptor isolated in a high-density lipoprotein particle efficiently activates its G protein
- PMID: 17452637
- PMCID: PMC1863461
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611448104
A monomeric G protein-coupled receptor isolated in a high-density lipoprotein particle efficiently activates its G protein
Abstract
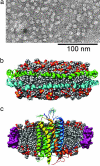
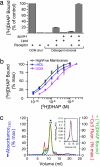
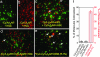
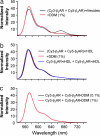
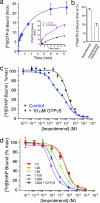
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) respond to a diverse array of ligands, mediating cellular responses to hormones and neurotransmitters, as well as the senses of smell and taste. The structures of the GPCR rhodopsin and several G proteins have been determined by x-ray crystallography, yet the organization of the signaling complex between GPCRs and G proteins is poorly understood. The observations that some GPCRs are obligate heterodimers, and that many GPCRs form both homo- and heterodimers, has led to speculation that GPCR dimers may be required for efficient activation of G proteins. However, technical limitations have precluded a definitive analysis of G protein coupling to monomeric GPCRs in a biochemically defined and membrane-bound system. Here we demonstrate that a prototypical GPCR, the beta2-adrenergic receptor (beta2AR), can be incorporated into a reconstituted high-density lipoprotein (rHDL) phospholipid bilayer particle together with the stimulatory heterotrimeric G protein, Gs. Single-molecule fluorescence imaging and FRET analysis demonstrate that a single beta2AR is incorporated per rHDL particle. The monomeric beta2AR efficiently activates Gs and displays GTP-sensitive allosteric ligand-binding properties. These data suggest that a monomeric receptor in a lipid bilayer is the minimal functional unit necessary for signaling, and that the cooperativity of agonist binding is due to G protein association with a receptor monomer and not receptor oligomerization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Catterall WA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:493–531. - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strubing C. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51:7–61. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. Cell. 2000;103:211–225. - PubMed
-
- Chabre M, le Maire M. Biochemistry. 2005;44:9395–9403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

