Alteration of the serum levels of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and head and neck carcinoma
- PMID: 17453000
- PMCID: PMC2359945
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603770
Alteration of the serum levels of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and head and neck carcinoma
Abstract
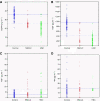
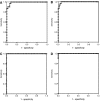
Serum levels of the soluble epidermal growth factor receptor (sEGFR) and its ligands epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-alpha) and amphiregulin (AR) were measured in healthy donors and patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and head and neck carcinoma (HNC). In NSCLC, we found sEGFR and EGF levels significantly lowered in patients with respect to healthy donors. In HNC patients, significantly diminished levels were found in the case of sEGFR, EGF and also AR. In both malignancies, no significant association was found between the serum levels of the molecules and the patients' gender, age or smoking habit. Only a significant association was found between the decrease of sEGFR and the absence of distant metastasis in NSCLC and the tumour stage in HNC. The most interesting result was that combining sEGFR and EGF, sensitivities of 88% in NSCLC and 100% in HNC were reached without losing specificity (97.8% in both cases). The use of discriminant analysis and logistic regression improved the sensitivity for NSCLC and the specificity for HNC. These data demonstrate a potentially interesting value of the serum levels of sEGFR and EGF, especially when combined, as markers for NSCLC and HNC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the prognostic value of soluble epidermal growth factor receptor plasma concentration in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients.Clin Lung Cancer. 2011 Sep;12(5):320-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2011.03.031. Epub 2011 May 11. Clin Lung Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21729651
-
Increases of amphiregulin and transforming growth factor-alpha in serum as predictors of poor response to gefitinib among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancers.Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 15;65(20):9176-84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1556. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16230376
-
Differential expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in primary non-small cell lung cancers and adjacent benign lung.Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2379-85. Cancer Res. 1993. PMID: 7683573
-
The EGF receptor system in head and neck carcinomas and normal tissues. Immunohistochemical and quantitative studies.Dan Med Bull. 1998 Apr;45(2):121-34. Dan Med Bull. 1998. PMID: 9587699 Review.
-
[Research Advances in CIMAvax-EGF for Non-small-cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2018 Jun 28;40(3):411-414. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2018.03.020. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 29978802 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
ErbB3 Ligand Heregulin1 Is a Major Mitogenic Factor for Uncontrolled Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation.Neoplasia. 2019 Apr;21(4):343-352. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 30831376 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of diverse signalling pathways by oncogenic PIK3CA mutations.Nat Commun. 2014 Sep 23;5:4961. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5961. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25247763 Free PMC article.
-
Photo-immobilized EGF chemical gradients differentially impact breast cancer cell invasion and drug response in defined 3D hydrogels.Biomaterials. 2018 Sep;178:751-766. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.01.032. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 29452913 Free PMC article.
-
Lapatinib-induced enhancement of mitochondrial respiration in HER2-positive SK-BR-3 cells: mechanism revealed by analysis of proteomic but not transcriptomic data.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Sep 30;11:1470496. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1470496. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39403185 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of EGFR, Her-2 and EGF in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a case control study.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 29;29(1):40. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-40. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20429940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron AT, Cora EM, Lafky JM, Boardman CH, Buenafe MC, Rademaker A, Dachao L, Fishman DA, Podratz KC, Maihle NJ (2003) Soluble epidermal growth factor receptor (sEGFR/sErbB1) as a potential risk, screening, and diagnostic serum biomarker of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 12: 103–113 - PubMed
-
- Baron AT, Lafky JM, Boardman CH, Balasubramaniam S, Suman VJ, Podratz KC, Nita JM (1999) Serum sErbB1 and epidermal growth factor levels as tumour biomarkers in women with stage III o IV epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 8: 129–137 - PubMed
-
- Baron AT, Lafky JM, Suman VJ, Hillman DW, Buenafe MC, Boardman CH, Podratz KC, Perz EA, Maihle NJ (2001) A preliminary study of serum concentrations of soluble epidermal growth factor receptor (sErbB1), gonadotropins, and steroid hormones in healthy men and women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 10: 1175–1185 - PubMed
-
- Baselga J (2002) Why the epidermal growth factor receptor? The rationale for cancer therapy. Oncologist 7: 2–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

