Ki-67 as prognostic marker in early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of published studies involving 12,155 patients
- PMID: 17453008
- PMCID: PMC2359936
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603756
Ki-67 as prognostic marker in early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of published studies involving 12,155 patients
Abstract
The Ki-67 antigen is used to evaluate the proliferative activity of breast cancer (BC); however, Ki-67's role as a prognostic marker in BC is still undefined. In order to better define the prognostic value of Ki-67/MIB-1, we performed a meta-analysis of studies that evaluated the impact of Ki-67/MIB-1 on disease-free survival (DFS) and/or on overall survival (OS) in early BC. Sixty-eight studies were identified and 46 studies including 12 155 patients were evaluable for our meta-analysis; 38 studies were evaluable for the aggregation of results for DFS, and 35 studies for OS. Patients were considered to present positive tumours for the expression of Ki-67/MIB-1 according to the cut-off points defined by the authors. Ki-67/MIB-1 positivity is associated with higher probability of relapse in all patients (HR=1.93 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.74-2.14); P<0.001), in node-negative patients (HR=2.31 (95% CI: 1.83-2.92); P<0.001) and in node-positive patients (HR=1.59 (95% CI: 1.35-1.87); P<0.001). Furthermore, Ki-67/MIB-1 positivity is associated with worse survival in all patients (HR=1.95 (95% CI: 1.70-2.24; P<0.001)), node-negative patients (HR=2.54 (95% CI: 1.65-3.91); P<0.001) and node-positive patients (HR=2.33 (95% CI: 1.83-2.95); P<0.001). Our meta-analysis suggests that Ki-67/MIB-1 positivity confers a higher risk of relapse and a worse survival in patients with early BC.
Figures
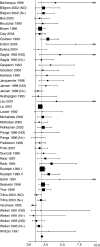

References
-
- Alonzo TA (2005) Standards for reporting prognostic tumor marker studies. J Clin Oncol 23: 9053–9054 - PubMed
-
- Beck T, Weller EE, Weikel W, Brumm C, Wilkens C, Knapstein PG (1995) Usefulness of immunohistochemical staining for p53 in the prognosis of breast carcinomas: correlations with established prognosis parameters and with the proliferation marker, MIB-1. Gynecol Oncol 57: 96–104 - PubMed
-
- Bevilacqua P, Verderio P, Barbareschi M, Bonoldi E, Boracchi P, Dalla Palma P, Gasparini G (1996) Lack of prognostic significance of the monoclonal antibody Ki-S1, a novel marker of proliferative activity, in node-negative breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 37: 123–133 - PubMed
-
- Biesterfeld S, Kluppel D, Koch R, Schneider S, Steinhagen G, Mihalcea AM, Schroder W (1998) Rapid and prognostically valid quantification of immunohistochemical reactions by immunohistometry of the most positive tumour focus. A prospective follow-up study on breast cancer using antibodies against MIB-1, PCNA, ER, and PR. J Pathol 185: 25–31 - PubMed
-
- Billgren AM, Tani E, Liedberg A, Skoog L, Rutqvist LE (2002) Prognostic significance of tumor cell proliferation analyzed in fine needle aspirates from primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 71: 161–170 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

