Mechanistic investigations of the dehydration reaction of lacticin 481 synthetase using site-directed mutagenesis
- PMID: 17455908
- PMCID: PMC2517115
- DOI: 10.1021/bi602663x
Mechanistic investigations of the dehydration reaction of lacticin 481 synthetase using site-directed mutagenesis
Abstract
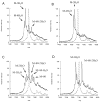
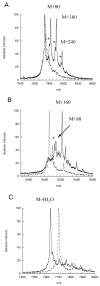
Lantibiotic synthetases catalyze the dehydration of Ser and Thr residues in their peptide substrates to dehydroalanine (Dha) and dehydrobutyrine (Dhb), respectively, followed by the conjugate addition of Cys residues to the Dha and Dhb residues to generate the thioether cross-links lanthionine and methyllanthionine, respectively. In this study ten conserved residues were mutated in the dehydratase domain of the best characterized family member, lacticin 481 synthetase (LctM). Mutation of His244 and Tyr408 did not affect dehydration activity with the LctA substrate whereas mutation of Asn247, Glu261, and Glu446 considerably slowed down dehydration and resulted in incomplete conversion. Mutation of Lys159 slowed down both steps of the net dehydration: phosphorylation of Ser/Thr residues and the subsequent phosphate elimination step to form the dehydro amino acids. Mutation of Arg399 to Met or Leu resulted in mutants that had phosphorylation activity but displayed greatly decreased phosphate elimination activity. The Arg399Lys mutant retained both activities, however. Similarly, the Thr405Ala mutant phosphorylated the LctA substrate but had compromised elimination activity. Finally, mutation of Asp242 or Asp259 to Asn led to mutant enzymes that lacked detectable dehydration activity. Whereas the Asp242Asn mutant retained phosphate elimination activity, the Asp259Asn mutant was not able to eliminate phosphate from a phosphorylated substrate peptide. A model is presented that accounts for the observed phenotypes of these mutant enzymes.
Figures


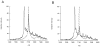



Similar articles
-
Using expressed protein ligation to probe the substrate specificity of lantibiotic synthetases.Methods Enzymol. 2009;462:117-34. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)62006-1. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19632472
-
Engineering dehydro amino acids and thioethers into peptides using lacticin 481 synthetase.Chem Biol. 2006 Oct;13(10):1109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.08.015. Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 17052615
-
The importance of the leader sequence for directing lanthionine formation in lacticin 481.Biochemistry. 2008 Jul 15;47(28):7342-51. doi: 10.1021/bi800277d. Epub 2008 Jun 21. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18570437 Free PMC article.
-
Lantibiotics: mode of action, biosynthesis and bioengineering.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009 Jan;10(1):2-18. doi: 10.2174/138920109787048616. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19149587 Review.
-
Mechanistic Understanding of Lanthipeptide Biosynthetic Enzymes.Chem Rev. 2017 Apr 26;117(8):5457-5520. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00591. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Chem Rev. 2017. PMID: 28135077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An engineered lantibiotic synthetase that does not require a leader peptide on its substrate.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Apr 25;134(16):6952-5. doi: 10.1021/ja3017297. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22480178 Free PMC article.
-
Lacticin 481 synthetase as a general serine/threonine kinase.ACS Chem Biol. 2009 May 15;4(5):379-85. doi: 10.1021/cb800309v. ACS Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19292452 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro mutasynthesis of lantibiotic analogues containing nonproteinogenic amino acids.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Sep 2;131(34):12024-5. doi: 10.1021/ja903239s. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19655738 Free PMC article.
-
Further Identification of Novel Lantibiotic Operons Using LanM-Based Genome Mining.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2011 Mar;3(1):27-40. doi: 10.1007/s12602-011-9062-y. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2011. PMID: 26781497
-
One-pot synthesis of class II lanthipeptide bovicin HJ50 via an engineered lanthipeptide synthetase.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 7;6:38630. doi: 10.1038/srep38630. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27924934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chatterjee C, Paul M, Xie L, van der Donk WA. Biosynthesis and Mode of Action of Lantibiotics. Chem Rev. 2005;105:633–684. - PubMed
-
- Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP. Bacterial lantibiotics: strategies to improve therapeutic potential. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005;6:61–75. - PubMed
-
- Schnell N, Entian K-D, Schneider U, Götz F, Zahner H, Kellner R, Jung G. Prepeptide sequence of epidermin, a ribosomally synthesized antibiotic with four sulphide-rings. Nature. 1988;278;333:276. - PubMed
-
- Xie L, Miller LM, Chatterjee C, Averin O, Kelleher NL, van der Donk WA. Lacticin 481: in vitro reconstitution of lantibiotic synthetase activity. Science. 2004;303:679–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

