PIASy controls ubiquitination-dependent proteasomal degradation of Ets-1
- PMID: 17456046
- PMCID: PMC2267315
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070026
PIASy controls ubiquitination-dependent proteasomal degradation of Ets-1
Abstract
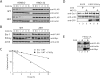
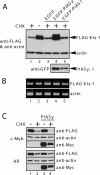
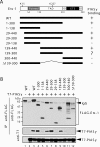
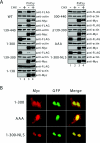
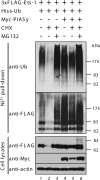
The ETS transcription factor Ets-1 (E26 transformation-specific-1) plays a critical role in many physiological processes including angiogenesis, haematopoietic development and tumour progression. Its activity can be regulated by post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation. Recently, we showed that Ets-1 is a target for SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) modification and that PIASy [protein inhibitor of activated STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) Y], a specific SUMO-E3 ligase for Ets-1, represses Ets-1-dependent transcription. In the present study, we demonstrated that Ets-1 is degraded by the proteasome and that overexpression of PIASy increased the stability of endogenous and ectopically expressed Ets-1 protein by preventing proteasomal degradation. Moreover, knockdown of the endogenous PIASy expression by RNA interference reduced the protein level of endogenous Ets-1. The proteasome inhibitor MG132 reversed this effect. Deletion analysis showed that the TAD (transcriptional activation domain), which has been identified as the interaction domain with PIASy, was also required for Ets-1 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. However, the Ets-1 stabilization by PIASy was not due to reduced ubiquitination of Ets-1. Our results suggested that PIASy controls Ets-1 function, at least in part, by inhibiting Ets-1 protein turnover via the ubiquitin-proteasome system.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Repression of E1AF transcriptional activity by sumoylation and PIASy.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Aug 17;360(1):226-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.06.037. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17585876
-
Id1 is down-regulated by hepatocyte growth factor via ERK-dependent and ERK-independent signaling pathways, leading to increased expression of p16INK4a in hepatoma cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Jul;7(7):1179-88. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0289. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19567783
-
The 26S proteasome system degrades the ERM transcription factor and regulates its transcription-enhancing activity.Oncogene. 2007 Jan 18;26(3):415-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209801. Epub 2006 Jul 10. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16832340
-
The measurement of ubiquitin and ubiquitinated proteins.Electrophoresis. 1999 Feb;20(2):418-28. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2683(19990201)20:2<418::AID-ELPS418>3.0.CO;2-N. Electrophoresis. 1999. PMID: 10197449 Review.
-
Novel initiation genes in squamous cell carcinomagenesis: a role for substrate-specific ubiquitylation in the control of cell survival.Mol Carcinog. 2007 Aug;46(8):585-90. doi: 10.1002/mc.20344. Mol Carcinog. 2007. PMID: 17626251 Review.
Cited by
-
B Cell Activation Results in IKK-Dependent, but Not c-Rel- or RelA-Dependent, Decreases in Transcription of the B Cell Tolerance-Inducing Gene Ets1.Immunohorizons. 2022 Nov 1;6(11):779-789. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2100065. Immunohorizons. 2022. PMID: 36445360 Free PMC article.
-
HECT-type ubiquitin ligase ITCH targets lysosomal-associated protein multispanning transmembrane 5 (LAPTM5) and prevents LAPTM5-mediated cell death.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 23;286(51):44086-44094. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.251694. Epub 2011 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22009753 Free PMC article.
-
Ets-1 as an early response gene against hypoxia-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Feb 19;6(2):e1650. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.8. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25695603 Free PMC article.
-
HUWE1 Causes an Immune Imbalance in Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura by Reducing the Number and Function of Treg Cells Through the Ubiquitination Degradation of Ets-1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 25;9:708562. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.708562. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34900980 Free PMC article.
-
Homeoprotein Msx1-PIASy Interaction Inhibits Angiogenesis.Cells. 2020 Aug 7;9(8):1854. doi: 10.3390/cells9081854. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32784646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Graves B. J., Petersen J. M. Specificity within the Ets family of transcription factors. Adv. Cancer Res. 1998;75:1–55. - PubMed
-
- Seth A., Ascione R., Fisher R. J., Mavrothalassitis G. J., Bhat N. K., Papas T. S. The Ets gene family. Cell Growth Differ. 1992;3:327–334. - PubMed
-
- Janknecht R., Nordheim A. Gene regulation by Ets proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1993;1155:346–356. - PubMed
-
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993;211:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Sharrocks A. D., Brown A. L., Ling Y., Yates P. R. The ETS-domain transcription factor family. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997;29:1371–1387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

